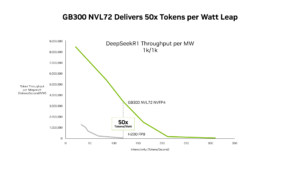
Editor’s note: This post is part of the AI Decoded series, which demystifies AI by making the technology more accessible, and showcases new hardware, software, tools and accelerations for RTX PC and workstation users.
Video is everywhere — nearly 80% of internet bandwidth today is used to stream video from content providers and social networks. While screens have become bigger and support higher resolutions, nearly all video is only 1080p quality or lower.
Upscalers can help sharpen streamed video and, powered by AI on the NVIDIA RTX platform, significantly enhance image quality and detail.
What Is an Upscaler?
The larger file size of videos makes it harder to compress and transmit compared to images or text. Platforms like Netflix, Vimeo and YouTube work around this limitation by encoding video — the process of compressing the raw source of a video into a smaller container format.
The encoder first analyzes the video to decide what information it can remove to make it fit a target resolution and frame rate. If the target bitrate is insufficient, the video quality decreases, resulting in a loss of detail and sharpness and the presence of encoding artifacts. The smaller the file, the easier it is to share on the internet — but the worse it looks.
Typically, software on the viewer’s device will upscale the video file to fit the display’s native resolution. However, these upscalers are fairly simplistic, merely multiplying pixels to meet the desired resolution. They can help sharpen the outlines of objects and scenes, but the final video typically carries encoding artifacts and sometimes looks over-sharpened and unnatural.
AI Know a Better Way
The NVIDIA RTX platform uses AI to easily de-artifact and upscale videos.
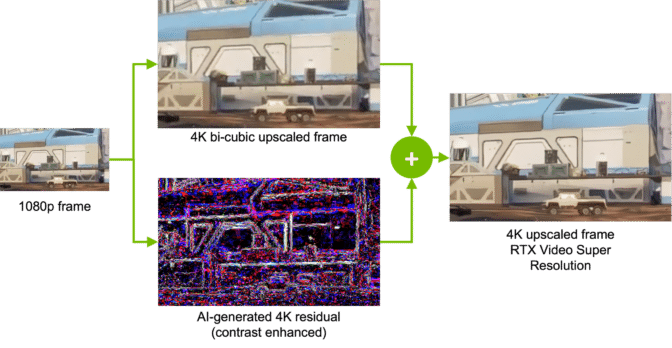
The process of AI upscaling involves analyzing images and motion vectors to generate new details not present in the original video. Instead of merely multiplying pixels, it recognizes the patterns of the image and enhances them to provide greater detail and video quality.
Images must be first de-artifacted before any processing begins. Artifacts — or unwanted distortions and anomalies that appear in video and image files — occur due to overcompression or data loss during transmission and storage.
NVIDIA AI networks can de-artifact images, helping remove blocky areas sometimes seen in streamed video. Without this first step, AI upscalers might end up enhancing the artifacted image itself instead of the desired content.
Super-Sized Video
Just like putting on a pair of prescription glasses can instantly snap the world into focus, RTX Video Super Resolution, one of NVIDIA’s latest innovations in AI-enhanced video technology, gives users a clearer picture into the world of streamed video.

Available on GeForce RTX 40 and 30 Series GPUs and RTX professional GPUs, it uses AI running on dedicated Tensor Cores to remove block compression artifacts and upscale lower-resolution content up to 4K, matching the user’s native display resolution.
RTX Video Super Resolution can be used to enhance all video watched on browsers. By combining de-artifacting with AI upscaling techniques, it can make even low-bitrate Twitch streams look stunningly clear. RTX Video Super Resolution is also supported in popular video apps like VLC so users can apply the same upscaling process to their offline videos.
Creators can soon use RTX Video Super Resolution in editing apps like Black Magic’s Davinci Resolve, making it easier than ever to upscale lower-quality video files to 4K resolution, as well as convert standard-dynamic range source files into high-dynamic range (HDR).
Say Hi to High-Dynamic Range
RTX Video now also supports AI HDR. HDR video supports a wider range of colors, lending greater detail especially to the darker and lighter areas of images. The problem is that there isn’t that much HDR content online yet.
Enter RTX Video HDR — by simply turning on the feature, the AI network will turn any standard or low-dynamic-range content into HDR, performing the correct tone mapping so the image still looks natural and retains its original colors.
AI Across the Board
RTX Video is just the latest implementation of AI upscaling powered by NVIDIA RTX.
Members of the GeForce NOW cloud streaming service can play their favorite PC games on nearly any device. GeForce RTX servers located all over the world first render the game video content, encode it and then stream it to the player’s local device — just like streaming video from other content providers.
Members on older NVIDIA GPU-powered devices can still use AI-enhanced upscaling to improve gameplay quality. This means they can enjoy the best of both worlds — gameplay rendered on servers powered by RTX 4080-class GPUs in the cloud and AI-enhanced streaming quality. Get more information on enabling AI-enhanced upscaling on GeForce NOW.
The NVIDIA SHIELD TV takes this one step further, processing AI neural networks directly on its NVIDIA Tegra system-on-a-chip to upscale 1080p-quality or lower content from nearly any streaming platform to a display’s native resolution. That means users can improve the video quality of content streamed from Netflix, Prime Video, Max, Disney+ and more at the push of a remote button.
SHIELD TV is currently available for up to $30 off in North America and £30 or 35€ off in Europe as part of Amazon’s Prime Day event running July 16-17. For Prime members in Europe, eligible SHIELD TV purchases also include one month of the GeForce NOW Ultimate membership for free, enabling GeForce RTX 4080-class PC gameplay streamed directly to the living room.
AI has enabled unprecedented improvements in video quality, helping set a new standard in streaming experiences.
Generative AI is transforming gaming, videoconferencing and interactive experiences of all kinds. Make sense of what’s new and what’s next by subscribing to the AI Decoded newsletter.