Putting on a pair of prescription glasses for the first time can feel like instantly snapping the world into focus.
Suddenly, trees have distinct leaves. Fine wrinkles and freckles show up on faces. Footnotes in books and even street names on roadside signs become legible.
Upscaling — converting lower resolution media to a higher resolution — offers a similar experience.
But with new AI upscaling techniques, the enhanced visuals look more crisp and realistic than ever.
Why Is Upscaling Necessary?
One-third of television-owning households in the U.S. have a 4K TV, known as ultra-high definition. But much of the content people watch on popular streaming services like YouTube, HBO and Netflix is only available at lower resolutions.

Standard definition video, widely used in TVs until the 1990s, was just 480 pixels high. High-definition TVs bumped that up to 720 or 1080 pixels — and is still the most common resolution format for content on TV and the web.
Owners of ultra-HD displays get the most out of their screens when watching 4K-mastered content. But when watching lower-resolution content, the video must be upscaled to fill out the entire display.
For example, 1080p images, known as full HD, have just a quarter of the pixels in 4K images. To display a 1080p shot from edge to edge on a 4K screen, the picture has to be stretched to match the TV’s pixels.
Upscaling is done by the streaming device being used — such as a smart TV or streaming media player. But typically, media players use basic upscaling algorithms that are unable to significantly improve high-definition content for 4K TVs.
What Is Basic Upscaling?
Basic upscaling is the simplest way of stretching a lower resolution image onto a larger display. Pixels from the lower resolution image are copied and repeated to fill out all the pixels of the higher resolution display.
Filtering is applied to smooth the image and round out unwanted jagged edges that may become visible due to the stretching. The result is an image that fits on a 4K display, but can often appear muted or blurry.
What Is AI Upscaling?
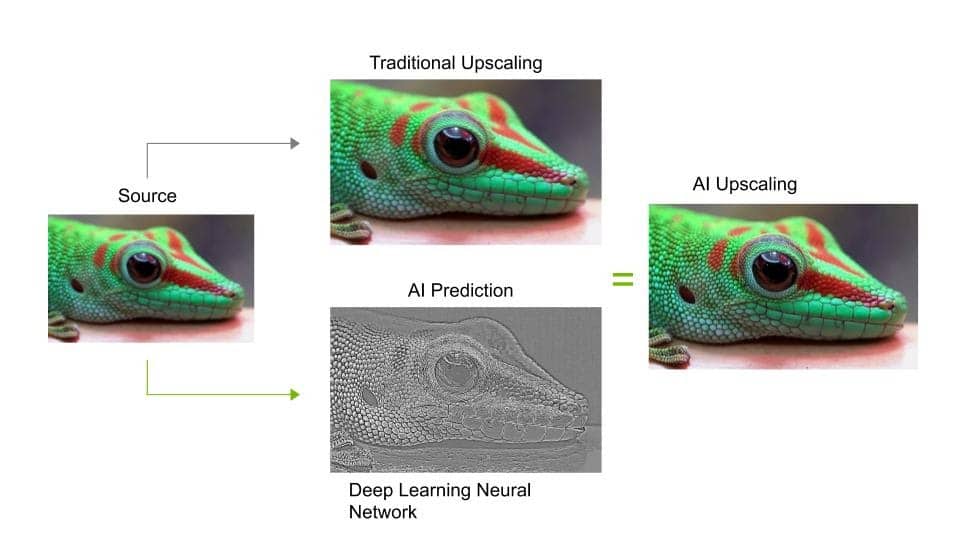
Traditional upscaling starts with a low-resolution image and tries to improve its visual quality at higher resolutions. AI upscaling takes a different approach: Given a low-resolution image, a deep learning model predicts a high-resolution image that would downscale to look like the original, low-resolution image.
To predict the upscaled images with high accuracy, a neural network model must be trained on countless images. The deployed AI model can then take low-resolution video and produce incredible sharpness and enhanced details no traditional scaler can recreate. Edges look sharper, hair looks scruffier and landscapes pop with striking clarity.
AI Upscaling on NVIDIA SHIELD TV
The NVIDIA SHIELD TV is the first streaming media player to feature AI upscaling. It can upscale 720p or 1080p HD content to 4K at up to 30 frames per second in real time.
Trained offline on a dataset of popular TV shows and movies, the model uses SHIELD’s NVIDIA Tegra X1+ processor for real-time inference. AI upscaling makes HD video content for top apps including HBO, Hulu, Netflix, Prime Video and YouTube appear sharper on 4K TVs, creating a more immersive viewing experience.
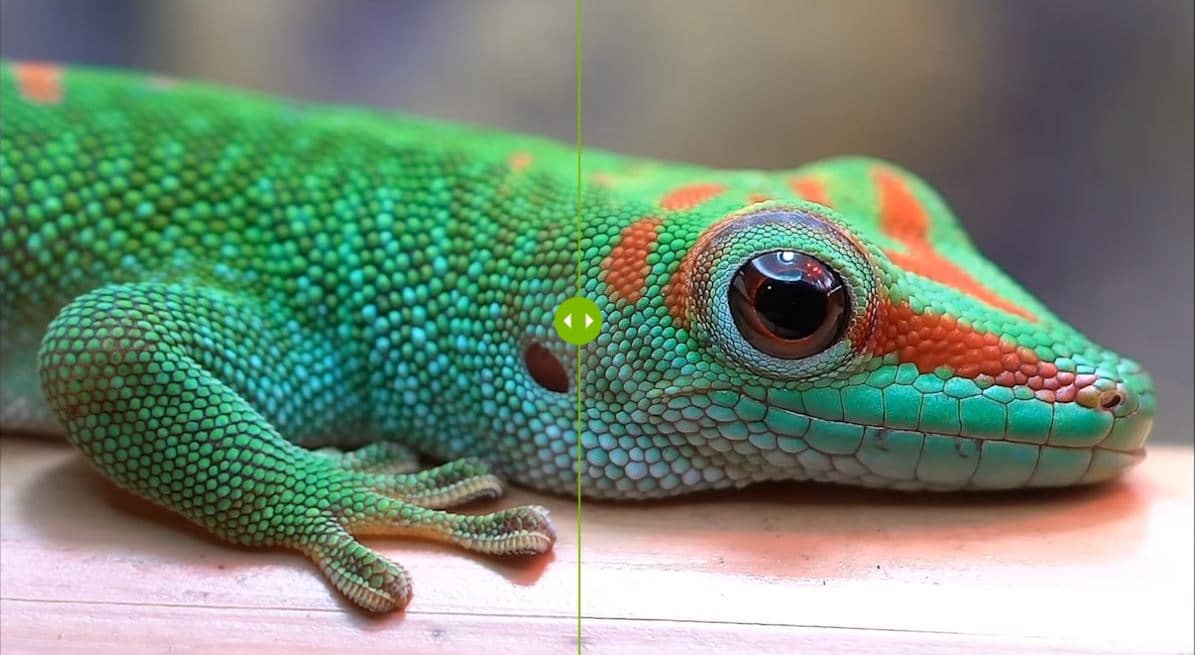
To see the difference between “basic upscaling” and “AI-enhanced upscaling” on SHIELD, click the image below and move the slider left and right.
NVIDIA SHIELD owners can toggle between basic and AI-enhanced modes in their device settings. A demo mode allows users to see a side-by-side comparison between regular content and AI-upscaled visuals. AI upscaling can be adjusted for high, medium or low detail enhancement — adjusting the confidence level of the neural network for detail prediction.
Learn more about upscaling on the NVIDIA SHIELD TV.