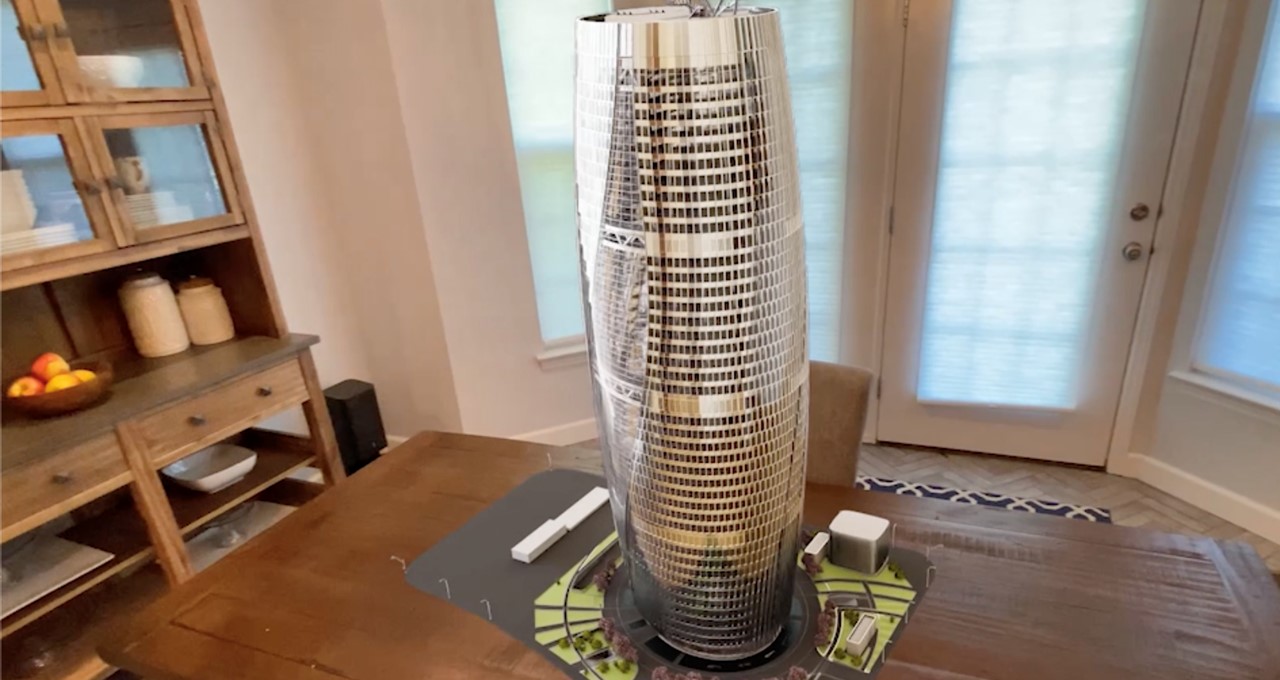
From design reviews with clients to construction rehearsals, virtual reality has proved its value in the architectural, engineering and construction industry. Viewing 3D models in a realistic, virtual 3D environment brings numerous benefits to design and visualization workflows.
However, the adoption of VR has been hampered by limitations such as the need to be tethered to a VR-ready workstation or having to work within a special tracking system. These requirements can limit where AEC firms set up VR sessions, and users can’t properly experience the immersive environment if they keep getting tangled in the tether.
NVIDIA CloudXR cuts the cord, delivering high-quality virtual and augmented reality experiences over networks to standalone headsets and devices. The latest NVIDIA CloudXR 3.0 release further extends access to AR and VR (often referred to as extended reality, or XR) by adding support for enhanced communication and collaboration among AEC teams. This allows users to enjoy a more comfortable XR experience – one that’s simpler to set up and safer to work in.
Enhancing Immersive Collaboration, From CloudXR to NVIDIA Omniverse
NVIDIA is driving the future of XR with CloudXR, enabling users to virtually work from anywhere without having to physically connect to powerful workstations. With CloudXR, professionals can experience benefits like the ability to view building designs without physical mockups, or visualize a multitude of materials and surfaces in various lighting conditions.
Architects using untethered VR headsets can freely move around digital building models without being constrained by cables. Teams can even send an inexpensive lightweight VR headset to customers and colleagues located a thousand miles away, so they can join the discussion using CloudXR’s bidirectional audio for collaboration.
Construction teams can more quickly and easily plan and rehearse construction workflows before tackling them in real life to identify risks and improve safety. Similarly, service and maintenance training simulations in VR helps technicians understand work processes more effectively than reading a manual or watching a video.
CloudXR also supports streaming from NVIDIA Omniverse, a groundbreaking real-time, RTX-powered simulation platform for 3D workflows that is transforming how architectural design teams collaborate. Globally dispersed project teams can use CloudXR and NVIDIA Omniverse to stream extended reality to low-cost, low-powered mobile devices anywhere in the world, while maintaining the high-quality experience traditionally reserved for high-performance computers.
Trailblazing the XR Path
Since the first portable head-mounted displays (HMDs) for VR came to market, NVIDIA has led the way in XR with the first VR-ready GPUs to deliver the high-graphics performance needed for stunning immersive experiences.
The latest NVIDIA RTX professional GPUs offer the performance and huge amount of VRAM that enable AEC teams to work with large, complex models in realistic environments. NVIDIA technologies like Variable Rate Super Sampling (VRSS) significantly improves VR image quality by allowing rendering resources to be focused in a foveated region with dynamic gaze tracking. And now, CloudXR is changing the game in AEC workflows.
Although standalone headsets, like the Oculus Quest 2, don’t need a high-end GPU to run, the image quality and experience is not as realistic due to the low level of compute power and insufficient memory, so it can’t always handle large datasets. But with CloudXR, all the GPU rendering and encoding is done on the server side instead of the client side.
CloudXR streams the data at the native resolution and refresh rate of the headset while handling the quality of service parameters of the network, so the user gets a high-quality experience as if directly tethered to a local workstation.
CloudXR also offers enhanced flexibility, as AEC companies have three options to power these streaming XR sessions:
- Use NVIDIA RTX-powered workstations that are specifically used for VR. A local machine can be configured as a server to stream the pixels with CloudXR over ethernet, Wi-Fi or a 5G network to an HMD, smartphone or tablet.
- Access CloudXR through a cloud service provider, such as Microsoft Azure, to stream XR content over high-performance networks to Windows, Android and iOS devices. Streaming AR content from the edge enables various use cases for the AEC industry — architectural design teams can overlay AR content on their physical-scale models to explore design options, or HVAC and electrical subcontractors can preview AR schematics using a tablet or smartphone while they’re onsite to map out installations in advance.
- Deploy the NVIDIA EGX Enterprise platform in a data center to deliver outstanding AR and VR experiences at the edge. The EGX platform with NVIDIA virtualization software is a great way for enterprises to drive these graphics-intensive types of workloads for their global teams. Streaming VR content from EGX servers in the data center to multiple remote HMDs also avoids the need for complex, time-consuming processes of VR technical experts setting up individual sessions.
Learn more about NVIDIA CloudXR for AEC.
Featured blog image: Leeza SOHO, Beijing, China. Image provided courtesy of Zaha Hadid Architects.