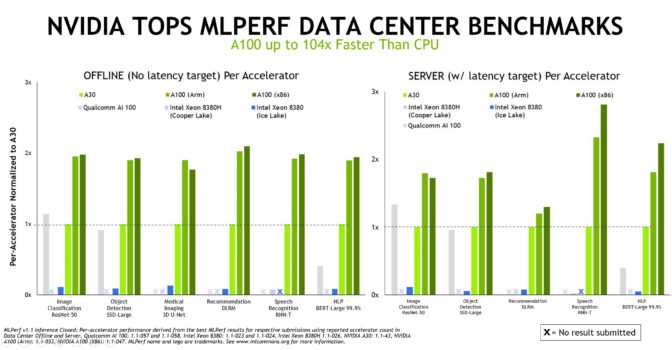
NVIDIA delivers the best results in AI inference using either x86 or Arm-based CPUs, according to benchmarks released today.
It’s the third consecutive time NVIDIA has set records in performance and energy efficiency on inference tests from MLCommons, an industry benchmarking group formed in May 2018.
And it’s the first time the data-center category tests have run on an Arm-based system, giving users more choice in how they deploy AI, the most transformative technology of our time.
Tale of the Tape
NVIDIA AI platform-powered computers topped all seven performance tests of inference in the latest round with systems from NVIDIA and nine of our ecosystem partners including Alibaba, Dell Technologies, Fujitsu, GIGABYTE, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Inspur Electronic Information, Lenovo, Nettrix and Supermicro.
And NVIDIA is the only company to report results on all MLPerf tests in this and every round to date.
Inference is what happens when a computer runs AI software to recognize an object or make a prediction. It’s a process that uses a deep learning model to filter data, finding results no human could capture.
MLPerf’s inference benchmarks are based on today’s most popular AI workloads and scenarios, covering computer vision, medical imaging, natural language processing, recommendation systems, reinforcement learning and more.
So, whatever AI applications they deploy, users can set their own records with NVIDIA.
Why Performance Matters
AI models and datasets continue to grow as AI use cases expand from the data center to the edge and beyond. That’s why users need performance that’s both dependable and flexible to deploy.
MLPerf gives users the confidence to make informed buying decisions. It’s backed by dozens of industry leaders, including Alibaba, Arm, Baidu, Google, Intel and NVIDIA, so the tests are transparent and objective.
Flexing Arm for Enterprise AI
The Arm architecture is making headway into data centers around the world, in part thanks to its energy efficiency, performance increases and expanding software ecosystem.
The latest benchmarks show that as a GPU-accelerated platform, Arm-based servers using Ampere Altra CPUs deliver near-equal performance to similarly configured x86-based servers for AI inference jobs. In fact, in one of the tests, the Arm-based server out-performed a similar x86 system.
NVIDIA has a long tradition of supporting every CPU architecture, so we’re proud to see Arm prove its AI prowess in a peer-reviewed industry benchmark.
“Arm, as a founding member of MLCommons, is committed to the process of creating standards and benchmarks to better address challenges and inspire innovation in the accelerated computing industry,” said David Lecomber, a senior director of HPC and tools at Arm.
“The latest inference results demonstrate the readiness of Arm-based systems powered by Arm-based CPUs and NVIDIA GPUs for tackling a broad array of AI workloads in the data center,” he added.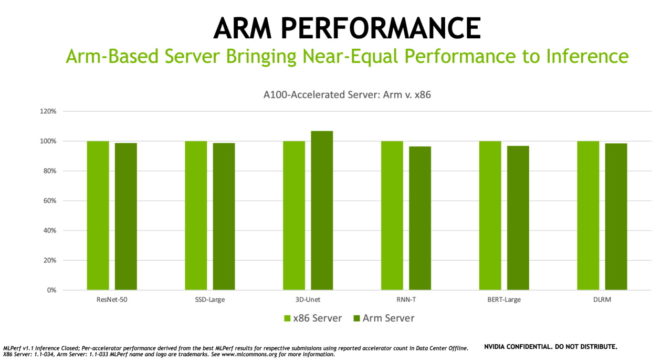
Partners Show Their AI Powers
NVIDIA’s AI technology is backed by a large and growing ecosystem.
Seven OEMs submitted a total of 22 GPU-accelerated platforms in the latest benchmarks.
Most of these server models are NVIDIA-Certified, validated for running a diverse range of accelerated workloads. And many of them support NVIDIA AI Enterprise, software officially released last month.
Our partners participating in this round included Dell Technologies, Fujitsu, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Inspur Electronic Information, Lenovo, Nettrix and Supermicro as well as cloud-service provider Alibaba.
The Power of Software
A key ingredient of NVIDIA’s AI success across all use cases is our full software stack.
For inference, that includes pre-trained AI models for a wide variety of use cases. The NVIDIA TAO Toolkit customizes those models for specific applications using transfer learning.
Our NVIDIA TensorRT software optimizes AI models so they make best use of memory and run faster. We routinely use it for MLPerf tests, and it’s available for both x86 and Arm-based systems.
We also employed our NVIDIA Triton Inference Server software and Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) capability in these benchmarks. They deliver for all developers the kind of performance that usually requires expert coders.
Thanks to continuous improvements in this software stack, NVIDIA achieved gains up to 20 percent in performance and 15 percent in energy efficiency from previous MLPerf inference benchmarks just four months ago.
All the software we used in the latest tests is available from the MLPerf repository, so anyone can reproduce our benchmark results. We continually add this code into our deep learning frameworks and containers available on NGC, our software hub for GPU applications.
It’s part of a full-stack AI offering, supporting every major processor architecture, proven in the latest industry benchmarks and available to tackle real AI jobs today.
To learn more about the NVIDIA inference platform, check out our NVIDIA Inference Technology Overview.