Generative AI applications have little, or sometimes negative, value without accuracy — and accuracy is rooted in data.
To help developers efficiently fetch the best proprietary data to generate knowledgeable responses for their AI applications, NVIDIA today announced four new NVIDIA NeMo Retriever NIM inference microservices.
Combined with NVIDIA NIM inference microservices for the Llama 3.1 model collection, also announced today, NeMo Retriever NIM microservices enable enterprises to scale to agentic AI workflows — where AI applications operate accurately with minimal intervention or supervision — while delivering the highest accuracy retrieval-augmented generation, or RAG.
NeMo Retriever allows organizations to seamlessly connect custom models to diverse business data and deliver highly accurate responses for AI applications using RAG. In essence, the production-ready microservices enable highly accurate information retrieval for building highly accurate AI applications.
For example, NeMo Retriever can boost model accuracy and throughput for developers creating AI agents and customer service chatbots, analyzing security vulnerabilities or extracting insights from complex supply chain information.
NIM inference microservices enable high-performance, easy-to-use, enterprise-grade inferencing. And with NeMo Retriever NIM microservices, developers can benefit from all of this — superpowered by their data.
These new NeMo Retriever embedding and reranking NIM microservices are now generally available:
- NV-EmbedQA-E5-v5, a popular community base embedding model optimized for text question-answering retrieval
- NV-EmbedQA-Mistral7B-v2, a popular multilingual community base model fine-tuned for text embedding for high-accuracy question answering
- Snowflake-Arctic-Embed-L, an optimized community model, and
- NV-RerankQA-Mistral4B-v3, a popular community base model fine-tuned for text reranking for high-accuracy question answering.
They join the collection of NIM microservices easily accessible through the NVIDIA API catalog.
Embedding and Reranking Models
NeMo Retriever NIM microservices comprise two model types — embedding and reranking — with open and commercial offerings that ensure transparency and reliability.
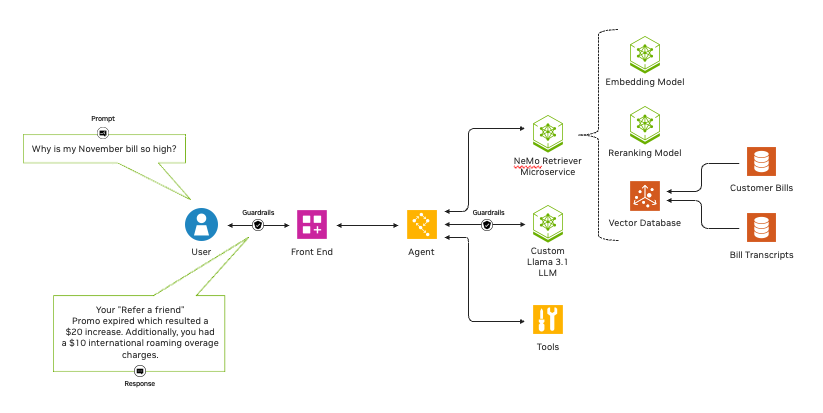
An embedding model transforms diverse data — such as text, images, charts and video — into numerical vectors, stored in a vector database, while capturing their meaning and nuance. Embedding models are fast and computationally less expensive than traditional large language models, or LLMs.
A reranking model ingests data and a query, then scores the data according to its relevance to the query. Such models offer significant accuracy improvements while being computationally complex and slower than embedding models.
NeMo Retriever provides the best of both worlds. By casting a wide net of data to be retrieved with an embedding NIM, then using a reranking NIM to trim the results for relevancy, developers tapping NeMo Retriever can build a pipeline that ensures the most helpful, accurate results for their enterprise.
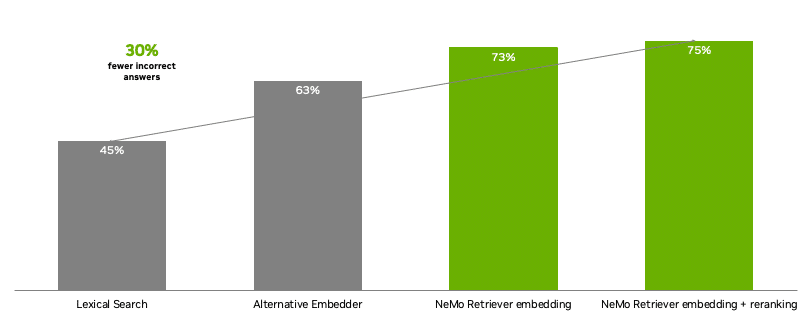
With NeMo Retriever, developers get access to state-of-the-art open, commercial models for building text Q&A retrieval pipelines that provide the highest accuracy. When compared with alternate models, NeMo Retriever NIM microservices provided 30% fewer inaccurate answers for enterprise question answering.
Top Use Cases
From RAG and AI agent solutions to data-driven analytics and more, NeMo Retriever powers a wide range of AI applications.
The microservices can be used to build intelligent chatbots that provide accurate, context-aware responses. They can help analyze vast amounts of data to identify security vulnerabilities. They can assist in extracting insights from complex supply chain information. And they can boost AI-enabled retail shopping advisors that offer natural, personalized shopping experiences, among other tasks.
NVIDIA AI workflows for these use cases provide an easy, supported starting point for developing generative AI-powered technologies.
Dozens of NVIDIA data platform partners are working with NeMo Retriever NIM microservices to boost their AI models’ accuracy and throughput.
DataStax has integrated NeMo Retriever embedding NIM microservices in its Astra DB and Hyper-Converged platforms, enabling the company to bring accurate, generative AI-enhanced RAG capabilities to customers with faster time to market.
Cohesity will integrate NVIDIA NeMo Retriever microservices with its AI product, Cohesity Gaia, to help customers put their data to work to power insightful, transformative generative AI applications through RAG.
Kinetica will use NVIDIA NeMo Retriever to develop LLM agents that can interact with complex networks in natural language to respond more quickly to outages or breaches — turning insights into immediate action.
NetApp is collaborating with NVIDIA to connect NeMo Retriever microservices to exabytes of data on its intelligent data infrastructure. Every NetApp ONTAP customer will be able to seamlessly “talk to their data” to access proprietary business insights without having to compromise the security or privacy of their data.
NVIDIA global system integrator partners including Accenture, Deloitte, Infosys, LTTS, Tata Consultancy Services, Tech Mahindra and Wipro, as well as service delivery partners Data Monsters, EXLService (Ireland) Limited, Latentview, Quantiphi, Slalom, SoftServe and Tredence, are developing services to help enterprises add NeMo Retriever NIM microservices into their AI pipelines.
Use With Other NIM Microservices
NeMo Retriever NIM microservices can be used with NVIDIA Riva NIM microservices, which supercharge speech AI applications across industries — enhancing customer service and enlivening digital humans.
New models that will soon be available as Riva NIM microservices include: FastPitch and HiFi-GAN for text-to-speech applications; Megatron for multilingual neural machine translation; and the record-breaking NVIDIA Parakeet family of models for automatic speech recognition.
NVIDIA NIM microservices can be used all together or separately, offering developers a modular approach to building AI applications. In addition, the microservices can be integrated with community models, NVIDIA models or users’ custom models — in the cloud, on premises or in hybrid environments — providing developers with further flexibility.
NVIDIA NIM microservices are available at ai.nvidia.com. Enterprises can deploy AI applications in production with NIM through the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform.
NIM microservices can run on customers’ preferred accelerated infrastructure, including cloud instances from Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, as well as NVIDIA-Certified Systems from global server manufacturing partners including Cisco, Dell Technologies, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Lenovo and Supermicro.
NVIDIA Developer Program members will soon be able to access NIM for free for research, development and testing on their preferred infrastructure.
Learn more about the latest in generative AI and accelerated computing by joining NVIDIA at SIGGRAPH, the premier computer graphics conference, running July 28-Aug. 1 in Denver.
See notice regarding software product information.
