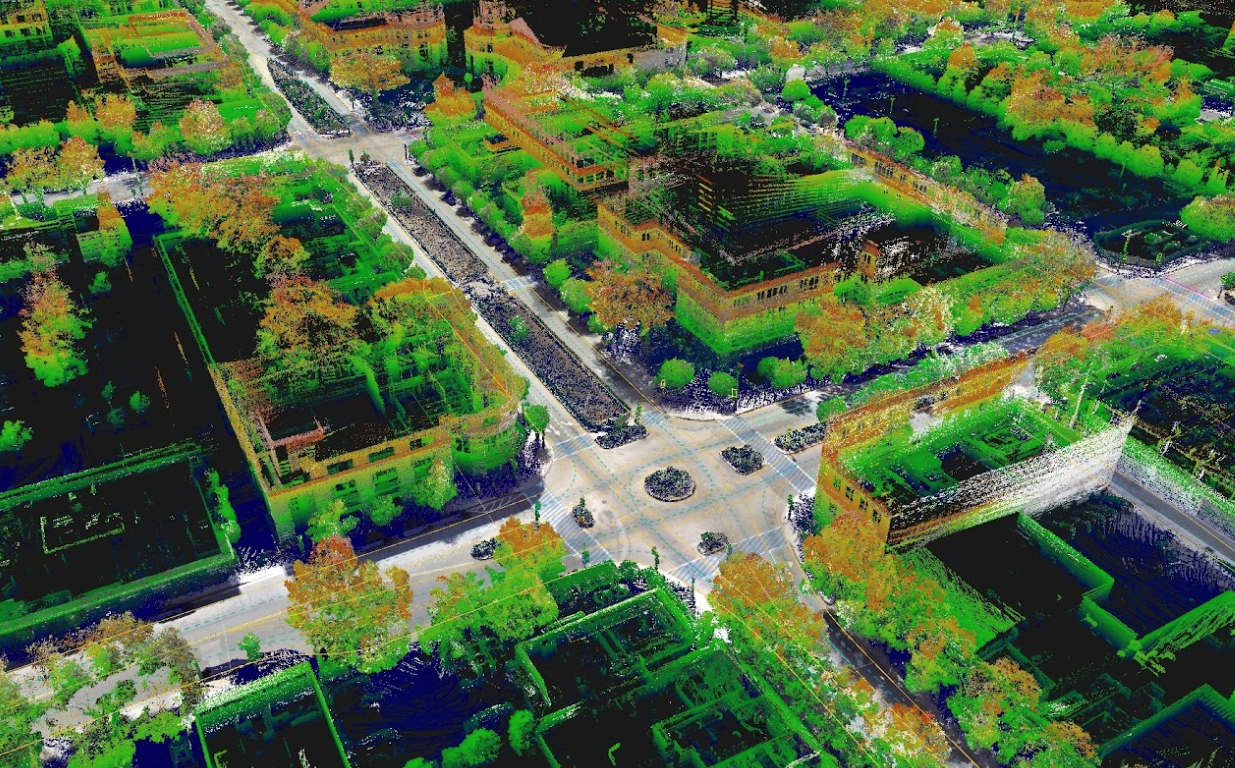
NVIDIA DRIVE Mapping is going global.
During the opening keynote at GTC, NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang demonstrated the latest mapping capabilities combining NVIDIA DRIVE and DeepMap technology. The result is a high-definition solution that enables crowdsourced maps for robust autonomous vehicle mapping and localization.
Mapping is a fundamental pillar for self-driving, serving as the collective memory of AVs. HD maps provide a baseline understanding of the driving environment and are continuously updated as the car drives. NVIDIA recently acquired leading mapping company DeepMap — together, these teams are accelerating, improving and extending high-performance mapping solutions worldwide.
These maps must be accurate within centimeters and reflect current road conditions, such as a work zone or a lane closure, and efficiently scale across AV fleets, with fast processing and minimal data storage. They must also be able to function worldwide.
NVIDIA DRIVE Mapping enables both AV fleets and individual vehicles to build and update maps in real time, creating a scalable solution for autonomous driving around the world.
A Continuous Cycle
DRIVE Mapping is built to be safe, scaleable and fresh.
The system leverages perception results from vehicles running NVIDIA DRIVE Hyperion 8, which includes the compute, sensors and software necessary for production autonomous vehicles. And, it covers a vehicle’s entire drive to support door-to-door autonomy at scale.
DRIVE Mapping includes both camera and radar localization layers in every region that is mapped for AI-assisted driving capabilities. Radar provides a layer of redundancy for localizing and driving in poor weather and lighting conditions where cameras may be blinded. To improve reliability and accuracy, the mapping networks are trained on ground-truth maps.
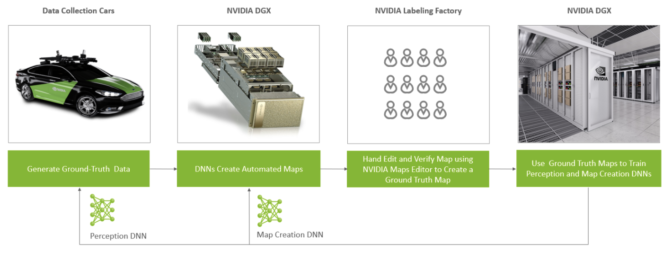
DRIVE Hyperion sensor data is fed into the NVIDIA DRIVE AGX AI compute platform inside the vehicle. Mapping networks use this data for perception, identifying intersection details, traffic lights, parking spots, and road and lane boundaries, and then determining safe driveable paths. These networks operate in a broad range of environments, lighting conditions, weather and geographies.
As a crowdsourced platform, DRIVE Mapping coverage grows along with the number of automakers that use NVIDIA DRIVE Hyperion. These automakers are on track to have fleets of vehicles distributed throughout the world, starting in 2024, and will continue to grow.
DRIVE Mapping leverages NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD infrastructure to maintain these maps at a global scale. These AI systems ingest terabytes of perception data from the DRIVE Hyperion vehicles to create and update maps.
The broad base of DRIVE Hyperion vehicles on the road, combined with robust perception, allows vehicles to detect road changes and keep maps fresh.
Developing with DeepMap
By leveraging the longstanding mapping expertise of DeepMap, which NVIDIA acquired earlier this year, DRIVE Mapping can scale worldwide, bringing safer, more efficient autonomous transportation to more roads.
Equipped with this extensive experience, NVIDIA is developing a dedicated fleet to build survey maps of the most populated areas of the world. These maps will prime future generations of AVs for real-time map creation.
With DRIVE Mapping, autonomous vehicles won’t just see the 3D world, but build it for continuous development and improvement.
Catch up on the full GTC keynote:
