With a detailed knowledge of the world and everything in it, maps provide the foresight AI uses to make advanced and safe driving decisions.
At his GTC keynote, NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang introduced NVIDIA DRIVE Map, a multimodal mapping platform designed to enable the highest levels of autonomy while improving safety. It combines the accuracy of DeepMap survey mapping with the freshness and scale of AI-based crowdsourced mapping.
With four localization layers — camera, lidar, radar and GNSS — DRIVE Map provides the redundancy and versatility required by the most advanced AI drivers.
DRIVE Map will provide survey-level ground truth mapping coverage to 500,000 kilometers of roadway in North America, Europe and Asia by 2024. This map will be continuously updated and expanded with millions of passenger vehicles.
NVIDIA DRIVE Map is available to the entire autonomous vehicle industry.
Multi-Layered
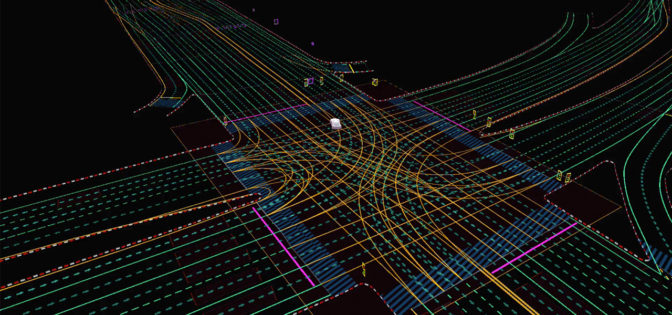
DRIVE Map contains multiple localization layers of data for use with camera, radar, lidar and GNSS modalities. The AI driver can localize to each layer of the map independently, providing the diversity and redundancy required for the highest levels of autonomy.
The camera localization layer consists of map attributes such as lane dividers, road markings, road boundaries, traffic lights, signs and poles.
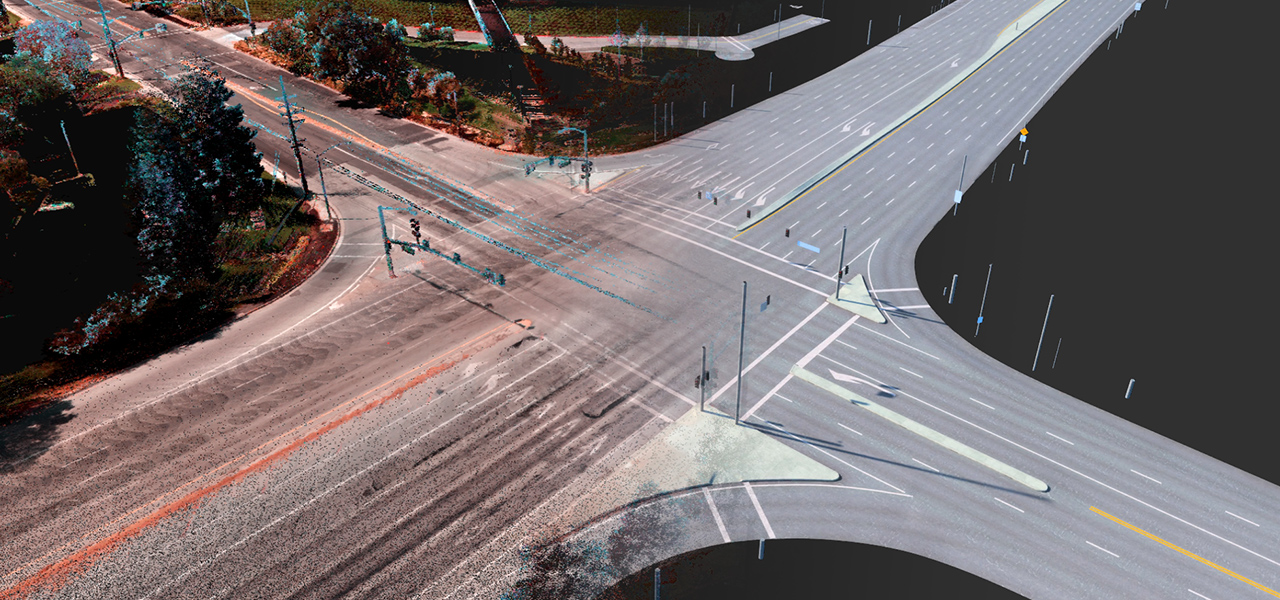
The radar localization layer is an aggregate point cloud of radar returns. It’s particularly useful in poor lighting conditions, which are challenging for cameras, and in poor weather conditions, which are challenging for cameras and lidars.
Radar localization is also useful in suburban areas where typical map attributes aren’t available, enabling the AI driver to localize based on surrounding objects that generate a radar return.
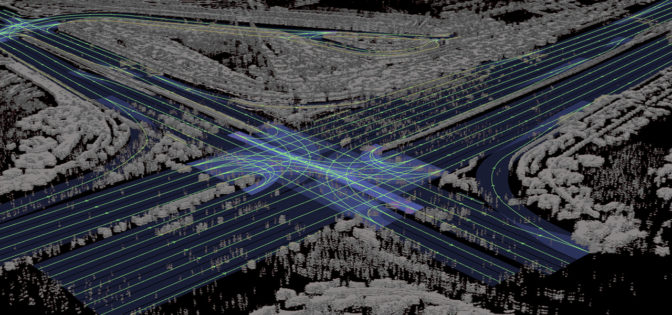
The lidar voxel layer provides the most precise and reliable representation of the environment. It builds a 3D representation of the world at 5-centimeter precision — accuracy very difficult to achieve with camera and radar.

The GNSS, or global navigation satellite system, layer provides information about the location, speed and orientation of the vehicle with high absolute accuracy and gathered from differential GNSS in data collection vehicles. This capability is particularly useful in bad weather conditions (rain, fog, snow, etc.) and on roads with limited markings.
Once localized to the map, the AI can use the detailed semantic information provided by the map to plan ahead and safely perform driving decisions.
Best of Both Worlds
DRIVE Map is built with two map engines — ground truth survey map engine and crowdsourced map engine — to gather and maintain a collective memory of an Earth-scale fleet.
This unique approach combines the best of both worlds, achieving centimeter-level accuracy with dedicated survey vehicles, as well as the freshness and scale that can only be achieved with millions of passenger vehicles continuously updating and expanding the map.
The ground truth engine is based on the DeepMap survey map engine — proven technology that has been developed and verified over the past six years.
The AI-based crowdsource engine gathers map updates from millions of cars, constantly uploading new data to the cloud as the vehicles drive. The data is then aggregated and used to update the map, providing the real-world fleet fresh over-the-air map updates.
DRIVE Map also provides a data interface, DRIVE MapStream, to allow any passenger car that meets the DRIVE Map requirements to continuously update the map using camera, radar and lidar data.
Earth-Scale Digital Twin
In addition to assisting the AI to make the optimal driving decisions, DRIVE Map accelerates AV deployment, from generating ground-truth training data for deep neural network training, as well as for testing and validation.
These workflows are centered on Omniverse, where real-world map data is loaded and stored. Omniverse maintains an Earth-scale representation of the digital twin that is continuously updated and expanded by survey map vehicles and millions of passenger vehicles.
Using automated content generation tools built on Omniverse, the detailed map is converted into a drivable simulation environment that can be used with NVIDIA DRIVE Sim. Features such as road elevation, road markings, islands, traffic signals, signs and vertical posts are accurately replicated at centimeter-level accuracy.
With physically based sensor simulation and domain randomization, AV developers can use the simulated environment to generate training scenarios that aren’t available in real data.
AV developers can also apply scenario generation tools to test AV software on digital twin environments before deploying AV in the real world. Finally, the digital twin provides fleet operators a complete virtual view of where the vehicles are driving in the world, assisting remote operation when needed.
As a highly versatile and scalable platform, DRIVE Map equips the AI driver with the understanding of the world needed to continuously advance autonomous capabilities.