Editor’s note: This post is part of a blog series highlighting NVIDIA AI Days across the globe.
NVIDIA AI Days — hosted for and in different pockets of the world — are drawing in hundreds of enthusiasts, developers, researchers and startups to discuss and explore the latest technologies making AI breakthroughs possible.
The latest stop: Tokyo, Japan.

Last week, over 900 attendees joined NVIDIA AI Day Tokyo to learn about sovereign AI — including two-dozen breakout sections on agentic and physical AI, quantum computing and AI factories.
NVIDIA Cloud Partners SoftBank, GMO Internet and KDDI each introduced the latest advancements to their AI factories and showcased how they’re supporting developers to build AI models and services.
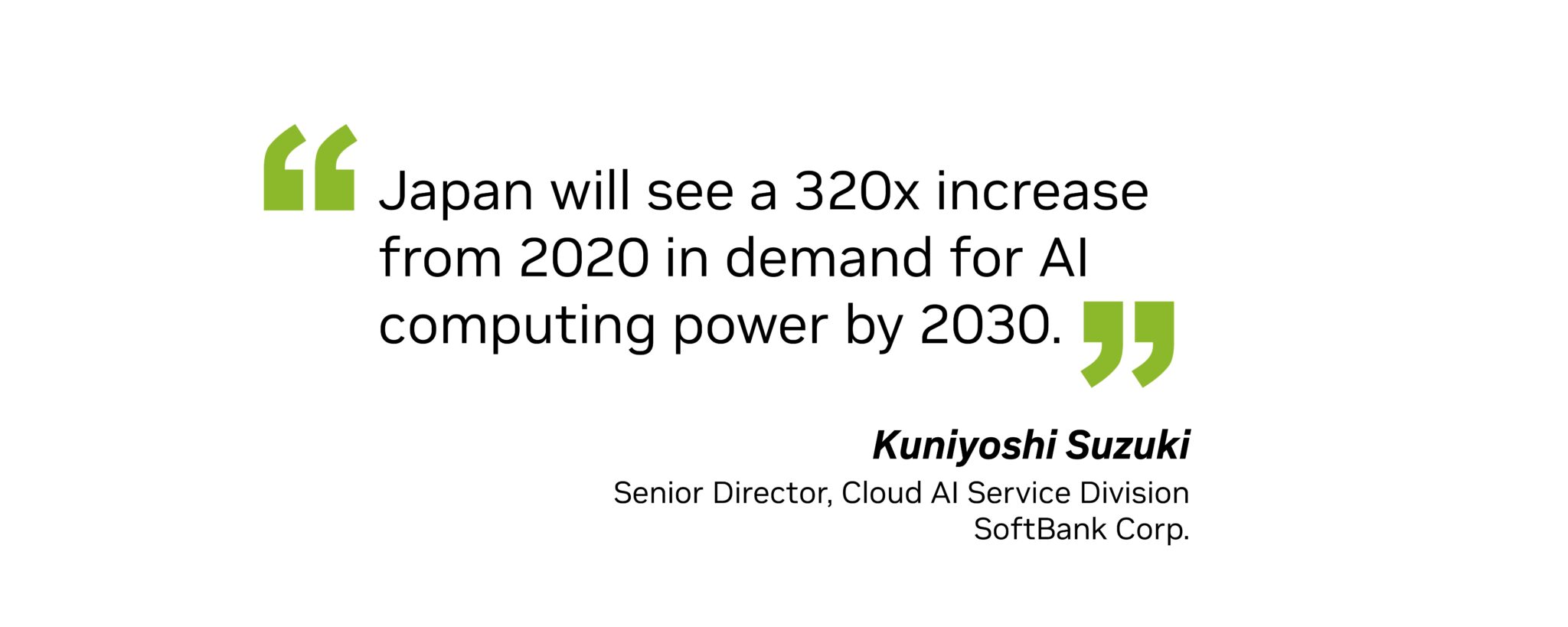
“Japan will see a 320x increase from 2020 in demand for AI computing power by 2030,” Kuniyoshi Suzuki, senior director of the cloud AI service division at SoftBank Corp., said at the event. “To ensure transparency and safety as AI adoption expands, it is crucial to build a foundation of domestic technologies — high performance, Japan-made large language models and large-scale domestic computing infrastructure capable of continuous LLM development.”
Why It Matters
The Japanese government is placing AI at the core of its national strategy. Last year, it announced a goal to invest at least 10 trillion yen — about $65 billion — through fiscal year 2030 to boost the semiconductor and AI industries.
“Specialized AI for industries like manufacturing, finance and healthcare will drive Japan’s digital transformation,” said Kazuya Ishikawa, evangelist of AI at NEC, a leader in IT and network technologies. “We are certain that LLMs such as NEC cotomi enable professional employees’ knowledge transfer or utilizing complex enterprise documents, directly addressing the skill gap and labor shortages that Japan is facing.”

Plus, Japan’s GENIAC initiative aims to strengthen domestic generative AI capabilities by providing companies with computing resources, fostering collaboration and supporting foundation model development — including LLMs tuned for the Japanese language and industry.
Here are some of the key players driving AI industry trends:
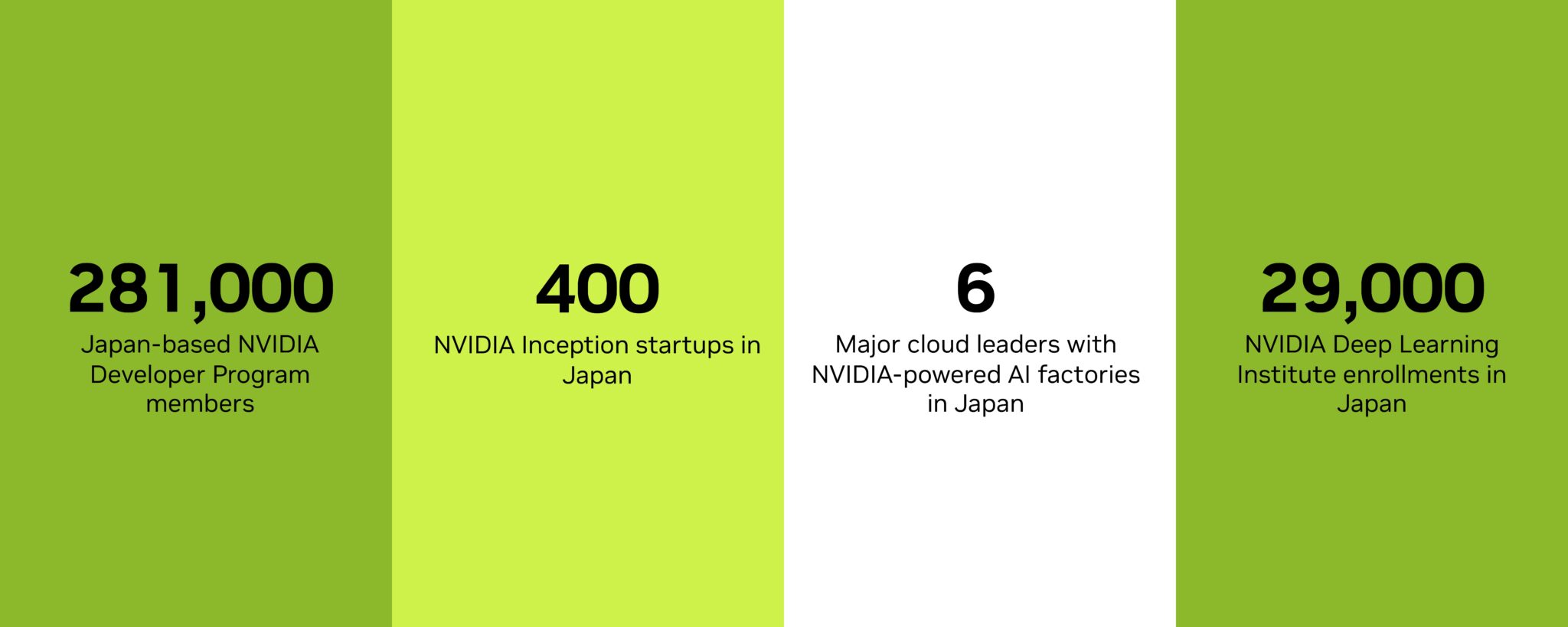
Industry in Motion
Japan-based NVIDIA partners are advancing the nation’s role in the next industrial revolution fueled by AI.
NVIDIA Inception members unveiled innovative services developed using the NVIDIA NeMo software suite.
For example, Stockmark announced the release of its 100-billion-parameter full-scratch Japanese LLM as an NVIDIA NIM microservice, offering 2.5x faster inference.
And FastLabel launched FastLabel Data Curation, a solution for developing autonomous-driving capabilities and advanced driver-assistance systems.
In addition, Hakuhodo Technologies, a service company of Japan’s major ad agency Hakuhodo, announced it will use NVIDIA AI Blueprints and the NVIDIA NeMo Agent toolkit to develop AI agents for autonomously producing advertisements.
Shimizu Corporation, a leading general contractor with over 200 years of history in Japan, revealed how it is exploring the NVIDIA AI Blueprint for video search and summarization to monitor work progress and potential risks at construction sites.
And an NVIDIA session at AI Day Tokyo highlighted the newly released Nemotron-Personas-Japan, the first open synthetic dataset aligned with Japan’s real-world demographic, geographic and cultural distributions. The dataset provides a privacy-preserving, regulation-ready foundation for sovereign AI systems to reflect Japanese society without relying on sensitive personal data.

“By leveraging advanced methodologies and accelerated computing, developers and businesses in Japan can empower AI agents to maximize enterprise data usage, drive organizational efficiency and achieve continuous innovation,” said Bartley Richardson, senior director of engineering at NVIDIA, who provided an overview of agentic AI at the event.

“Japanese developers are building flexible and powerful agentic systems suitable for Japan’s drive toward technological excellence and operational precision,” he added.

Other Event Highlights
A special “Japan Healthcare Day” provided deep dives into NVIDIA’s healthcare technologies for developers and researchers from Japan’s medtech companies.
Four sessions covered how the open-source MONAI framework, along with the NVIDIA Holoscan and NVIDIA Isaac for Healthcare platforms, are accelerating the development of cutting-edge medical devices and digital health tools with agentic AI.
Training workshops from the NVIDIA Deep Learning Institute covered building AI agents with retrieval-augmented generation capabilities using LLMs and an introduction to the NVIDIA Cosmos world foundation model platform for physical AI.
The event also included a meetup where startups from the NVIDIA Inception program met with NVIDIA Cloud Partners to identify suitable partners for their developer environment. The startups also connected with venture capital companies.
What’s Next
Building on its strength in engineering and mechatronics, Japan is poised to drive a new era where advanced digital agents capable of planning, reasoning and collaborating will become digital workers to execute complex tasks alongside physical AI.
Physical AI lets autonomous systems like cameras, robots and self-driving cars perceive, understand, reason and perform or orchestrate complex actions in the real world.
The physical AI track at AI Day Tokyo provided insights on technologies such as NVIDIA Omniverse for digital twins, NVIDIA Isaac GR00T for humanoid robotics development and NVIDIA Cosmos world foundation models.
Next up: NVIDIA AI Day Sydney, running Oct. 15-16, where attendees can learn about the latest AI breakthroughs, connect with peers and experts, and contribute to the next wave of innovation.
Explore more content from AI Days around the globe.




