From the stages of the PyTorch Conference to hackathons and workshops, Open Source AI Week spotlighted the innovation, collaboration and community driving open-source AI forward.
Here are some highlights from the event:
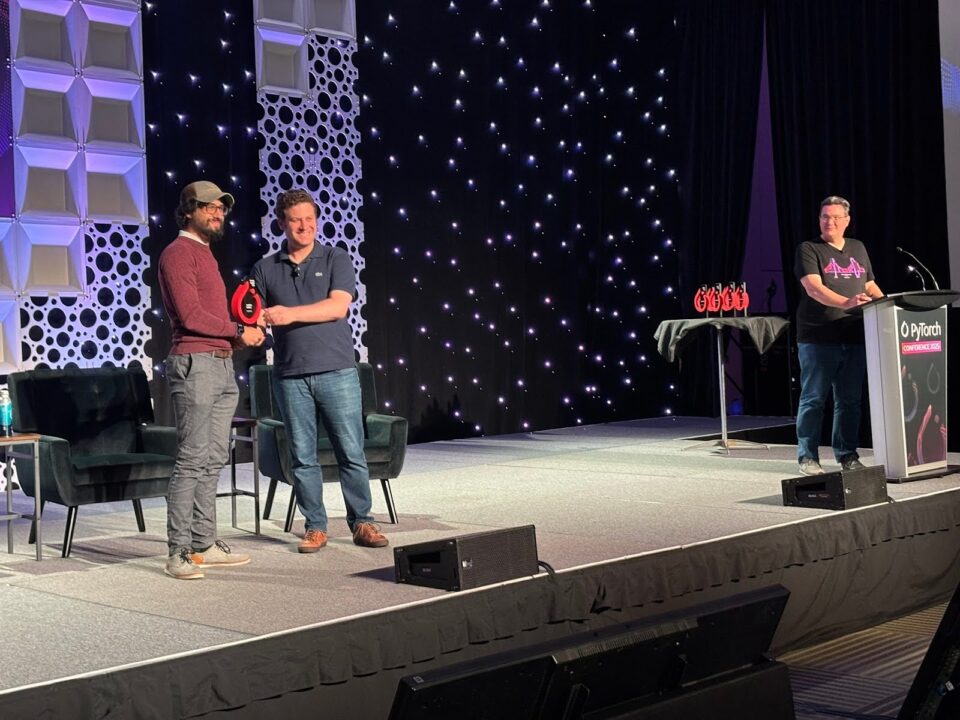
Honoring open-source contributions: Jonathan Dekhtiar, senior deep learning framework engineer at NVIDIA, received the PyTorch Contributor Award for his key role in designing the release mechanisms and packaging solutions for Python software and libraries that enable GPU-accelerated computing.
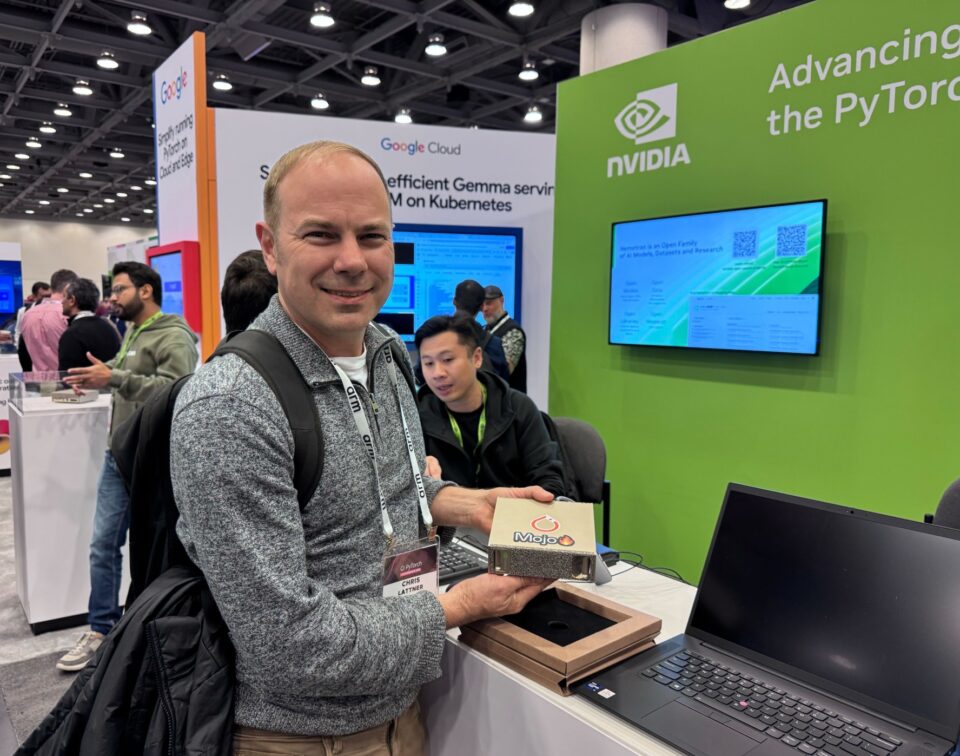
CEO of Modular visits the NVIDIA booth: Chris Lattner, CEO of Modular and founder and chief architect of the open-source LLVM Compiler Infrastructure project, picks up the NVIDIA DGX Spark.
Seven questions with founding researcher at fast.ai: Jeremy Howard, founding researcher at fast.ai and advocate for accessible deep learning, shares his insights on the future of open-source AI.
In his keynote at the PyTorch Conference, Howard also highlighted the growing strength of open-source communities, recognizing NVIDIA for its leadership in advancing openly available, high-performing AI models.
“The one company, actually, that has stood out, head and shoulders above the others, and that is two,” he said. “One is Meta…the creators of PyTorch. The other is NVIDIA, who, just in recent months, has created some of the world’s best models — and they are open source, and they are openly licensed.”
vLLM Adds Upstream Support for NVIDIA Nemotron Models 🔗
Open-source innovation is accelerating. NVIDIA and the vLLM team are partnering to add vLLM upstream support for NVIDIA Nemotron models, transforming open large language model (LLM) serving with lightning-fast performance, efficient scaling and simplified deployment across NVIDIA GPUs.
vLLM’s optimized inference engine empowers developers to run Nemotron models like the new Nemotron Nano 2 — a highly efficient small language reasoning model with a hybrid Transformer-Mamba architecture and a configurable thinking budget.
Learn more about how vLLM is accelerating open model innovation.
NVIDIA Expands Open Access to Nemotron RAG Models 🔗
NVIDIA is making eight NVIDIA Nemotron RAG models openly available on Hugging Face, expanding access beyond research to include the full suite of commercial models.
This release gives developers a wider range of tools to build retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, improve search and ranking accuracy, and extract structured data from complex documents.
The newly released models include Llama-Embed-Nemotron-8B, which provides multilingual text embeddings built on Llama 3.1, and Omni-Embed-Nemotron-3B, which supports cross-modal retrieval for text, images, audio and video.
Developers can also access six production-grade models for text embedding, reranking and PDF data extraction — key components for real-world retrieval and document intelligence applications.
With these open-source models, developers, researchers and organizations can more easily integrate and experiment with RAG-based systems.
Developers can get started with Nemotron RAG on Hugging Face.
Building and Training AI Models With the Latest Open Datasets 🔗
NVIDIA is expanding access to high-quality open datasets that help developers overcome the challenges of large-scale data collection and focus on building advanced AI systems.
The latest release includes a collection of Nemotron-Personas datasets for Sovereign AI. Each dataset is fully synthetic and grounded in real-world demographic, geographic and cultural data — with no personally identifiable information. The growing collection, which features personas from the U.S., Japan and India, enables model builders to design AI agents and systems that reflect the linguistic, social and contextual nuance of the nations they serve.
NVIDIA earlier this year released the NVIDIA Physical AI Open Datasets on Hugging Face, featuring more than 7 million robotics trajectories and 1,000 OpenUSD SimReady assets. Downloaded more than 6 million times, the datasets combines real‑world and synthetic data from the NVIDIA Cosmos, Isaac, DRIVE and Metropolis platforms to kickstart physical AI development.
NVIDIA Inception Startups Highlight AI Innovation 🔗
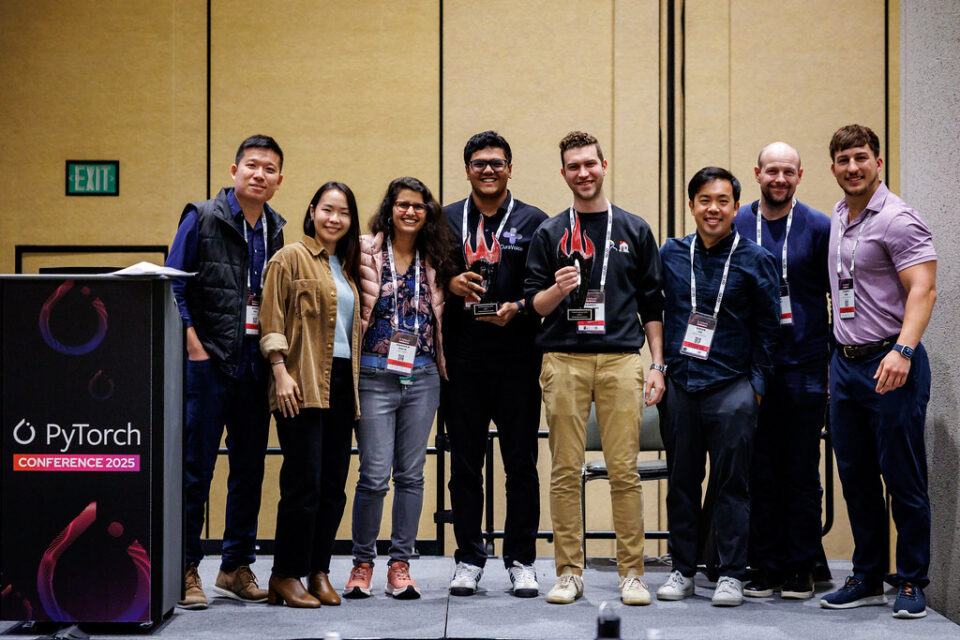
At the PyTorch Conference’s Startup Showcase, 11 startups — including members from the NVIDIA Inception program — are sharing their work developing practical AI applications and connecting with investors, potential customers and peers.
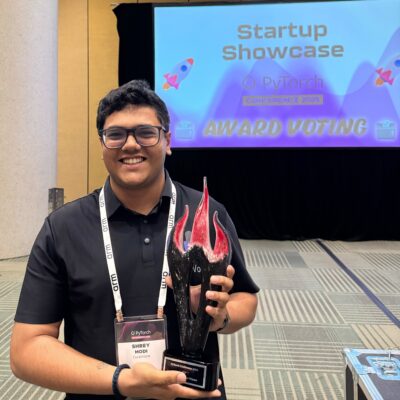
Runhouse, an AI infrastructure startup optimizing model deployment and orchestration, was crowned the 2025 PyTorch Startup Showcase Award Winner. The Community Choice Award was presented to CuraVoice, with CEO Sakhi Patel, CTO Shrey Modi, and advisor Rahul Vishwakarma accepting the award on behalf of the team.
CuraVoice provides an AI-powered voice simulation platform — powered by NVIDIA Riva for speech recognition and text-to-speech, and NVIDIA NeMo for conversational AI models — for healthcare students and professionals, offering interactive exercises and adaptive feedback to improve patient communication skills.

In addition to CuraVoice, other Inception members, including Backfield AI, Graphsignal, Okahu AI, Snapshot AI and XOR, were featured participants in the Startup Showcase.
Snapshot AI delivers actionable, real-time insights to engineering teams using recursive RAG, transformers and multimodal AI. The company’s platform taps into the NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit to deliver high-performance analysis and rapid insights at scale.
XOR is a cybersecurity startup offering AI agents that automatically fix vulnerabilities in the supply chain of other AIs. The company helps enterprises eliminate vulnerabilities while complying with regulatory requirements. XOR’s agentic technology uses NVIDIA cuVS vector search for indexing, real-time retrieval and code analysis. The company also uses GPU-based machine learning to train models to detect hidden backdoor patterns and prioritize of high-value security outcomes.

Highlights From Open Source AI Week 🔗
Attendees of Open Source AI Week are getting a peek at the latest advancements and creative projects that are shaping the future of open technology.
Here’s a look at what’s happening onsite:
The world’s smallest AI supercomputer: NVIDIA DGX Spark represents the cutting edge of AI computing hardware for enterprise and research applications.
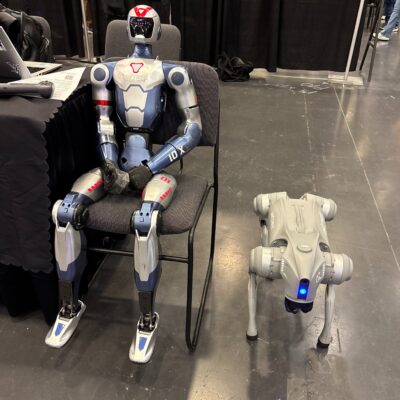
Humanoids and robot dogs, up close: Unitree robots are on display, captivating attendees with advanced mobility powered by the latest robotics technology.
Why open source is important: Learn how it can empower developers to build stronger communities, iterate on features, and seamlessly integrate the best of open source AI.
Accelerating AI Research Through Open Models 🔗
A study from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET) published today shows how access to open model weights unlocks more opportunities for experimentation, customization and collaboration across the global research community.
The report outlines seven high-impact research use cases where open models are making a difference — including fine-tuning, continued pretraining, model compression and interpretability.
With access to weights, developers can adapt models for new domains, explore new architectures and extend functionality to meet their specific needs. This also supports trust and reproducibility. When teams can run experiments on their own hardware, share updates and revisit earlier versions, they gain control and confidence in their results.
Additionally, the study found that nearly all open model users share their data, weights and code, building a fast-growing culture of collaboration. This open exchange of tools and knowledge strengthens partnerships between academia, startups and enterprises, facilitating innovation.
NVIDIA is committed to empowering the research community through the NVIDIA Nemotron family of open models — featuring not just open weights, but also pretraining and post-training datasets, detailed training recipes, and research papers that share the latest breakthroughs.
Read the full CSET study to learn how open models are helping the AI community move forward.
Advancing Embodied Intelligence Through Open-Source Innovation 🔗
At the PyTorch Conference, Jim Fan, director of robotics and distinguished research scientist at NVIDIA, discussed the Physical Turing Test — a way of measuring the performance of intelligent machines in the physical world.
With conversational AI now capable of fluent, lifelike communication, Fan noted that the next challenge is enabling machines to act with similar naturalism. The Physical Turing Test asks: can an intelligent machine perform a real-world task so fluidly that a human cannot tell whether a person or a robot completed it?
Fan highlighted that progress in embodied AI and physical AI depends on generating large amounts of diverse data, access to open robot foundation models and simulation frameworks — and walked through a unified workflow for developing embodied AI.
With synthetic data workflows like NVIDIA Isaac GR00T-Dreams — built on NVIDIA Cosmos world foundation models— developers can generate virtual worlds from images and prompts, speeding the creation of large sets of diverse and physically accurate data.
That data can then be used to post-train NVIDIA Isaac GR00T N open foundation models for generalized humanoid robot reasoning and skills. But before the models are deployed in the real world, these new robot skills need to be tested in simulation.
Open simulation and learning frameworks such as NVIDIA Isaac Sim and Isaac Lab allow robots to “practice” countless times across millions of virtual environments before operating in the real world, dramatically accelerating learning and deployment cycles.
Plus, with Newton, an open-source, differentiable physics engine built on NVIDIA Warp and OpenUSD, developers can bring high-fidelity simulation to complex robotic dynamics such as motion, balance and contact — reducing the simulation-to-real gap.
This accelerates the creation of physically capable AI systems that learn faster, perform more safely and operate effectively in real-world environments.
However, scaling embodied intelligence isn’t just about compute — it’s about access. Fan reaffirmed NVIDIA’s commitment to open source, emphasizing how the company’s frameworks and foundation models are shared to empower developers and researchers globally.
Developers can get started with NVIDIA’s open embodied and physical AI models on Hugging Face.
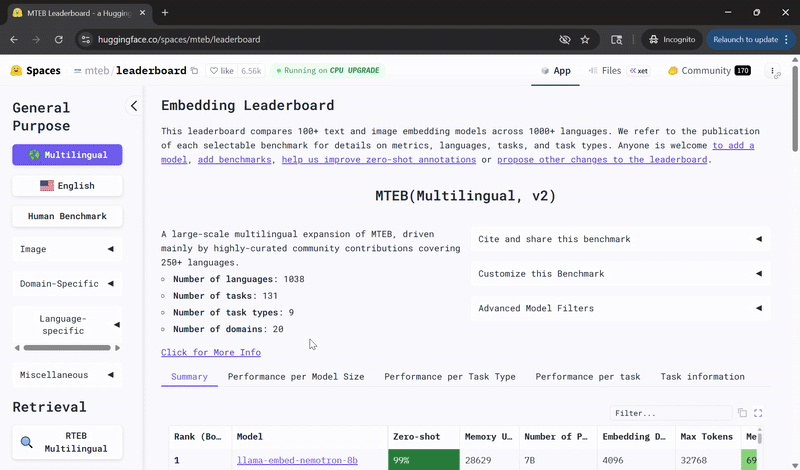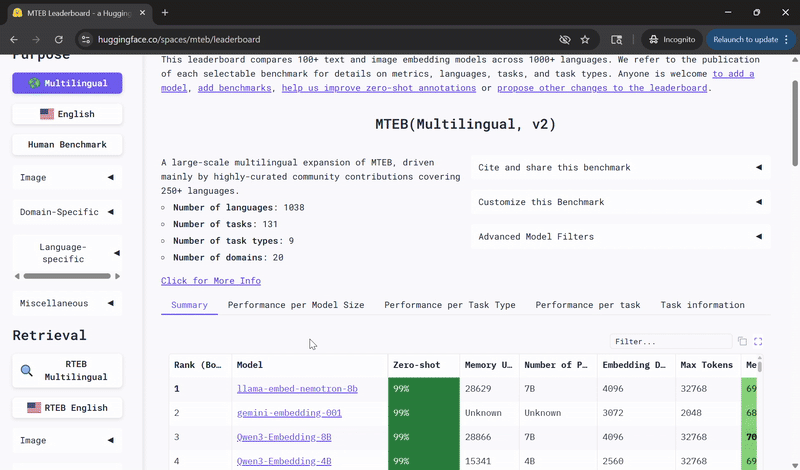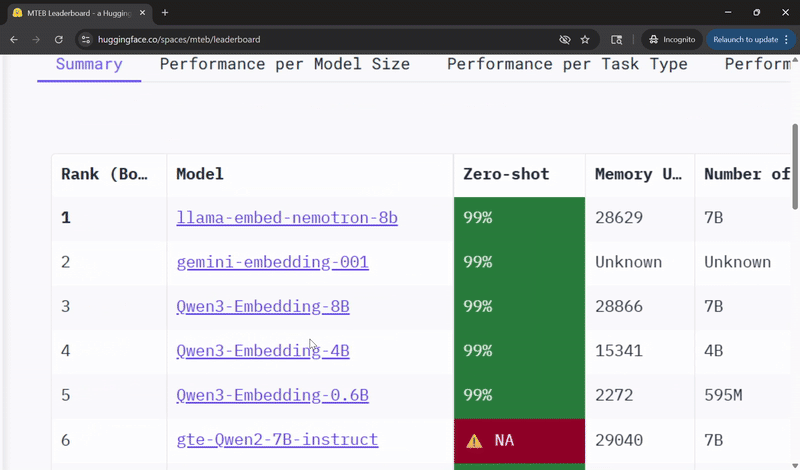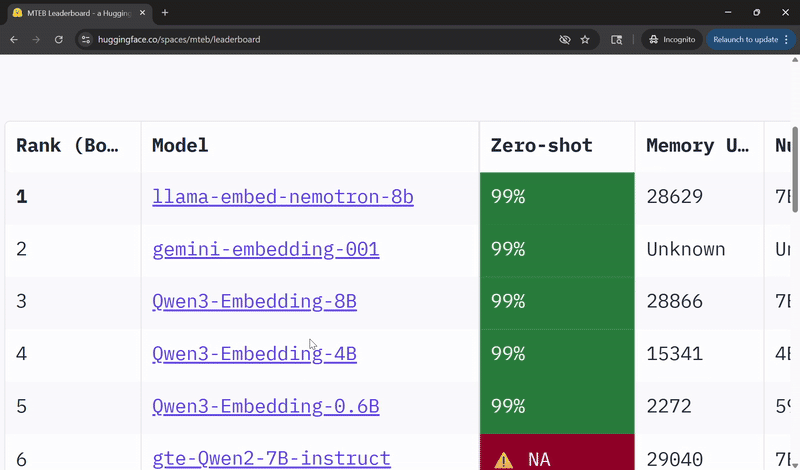
Llama‑Embed‑Nemotron‑8B Ranks Among Top Open Models for Multilingual Retrieval 🔗
NVIDIA’s Llama‑Embed‑Nemotron‑8B model has been recognized as the top open and portable model on the Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark leaderboard.
Built on the meta‑llama/Llama‑3.1‑8B architecture, Llama‑Embed‑Nemotron‑8B is a research text embedding model that converts text into 4,096‑dimensional vector representations. Designed for flexibility, it supports a wide range of use cases, including retrieval, reranking, semantic similarity and classification across more than 1,000 languages.
Trained on a diverse collection of 16 million query–document pairs — half from public sources and half synthetically generated — the model benefits from refined data generation techniques, hard‑negative mining and model‑merging approaches that contribute to its broad generalization capabilities.
This result builds on NVIDIA’s ongoing research in open, high‑performing AI models. Following earlier leaderboard recognition for the Llama NeMo Retriever ColEmbed model, the success of Llama‑Embed‑Nemotron‑8B highlights the value of openness, transparency and collaboration in advancing AI for the developer community.
Check out Llama-Embed-Nemotron-8B on Hugging Face, and learn more about the model, including architectural highlights, training methodology and performance evaluation.
What Open Source Teaches Us About Making AI Better
Open models are shaping the future of AI, enabling developers, enterprises and governments to innovate with transparency, customization and trust. In the latest episode of the NVIDIA AI Podcast, NVIDIA’s Bryan Catanzaro and Jonathan Cohen discuss how open models, datasets and research are laying the foundation for shared progress across the AI ecosystem.
The NVIDIA Nemotron family of open models represents a full-stack approach to AI development, connecting model design to the underlying hardware and software that power it. By releasing Nemotron models, data and training methodologies openly, NVIDIA aims to help others refine, adapt and build upon its work, resulting in a faster exchange of ideas and more efficient systems.
“When we as a community come together — contributing ideas, data and models — we all move faster,” said Catanzaro in the episode. “Open technologies make that possible.”
There’s more happening this week at Open Source AI Week, including the start of the PyTorch Conference — bringing together developers, researchers and innovators pushing the boundaries of open AI.
Attendees can tune in to the special keynote address by Jim Fan, director of robotics and distinguished research scientist at NVIDIA, to hear the latest advancements in robotics — from simulation and synthetic data to accelerated computing. The keynote, titled “The Physical Turing Test: Solving General Purpose Robotics,” will take place on Wednesday, Oct. 22, from 9:50-10:05 a.m. PT.
Andrej Karpathy’s Nanochat Teaches Developers How to Train LLMs in Four Hours 🔗
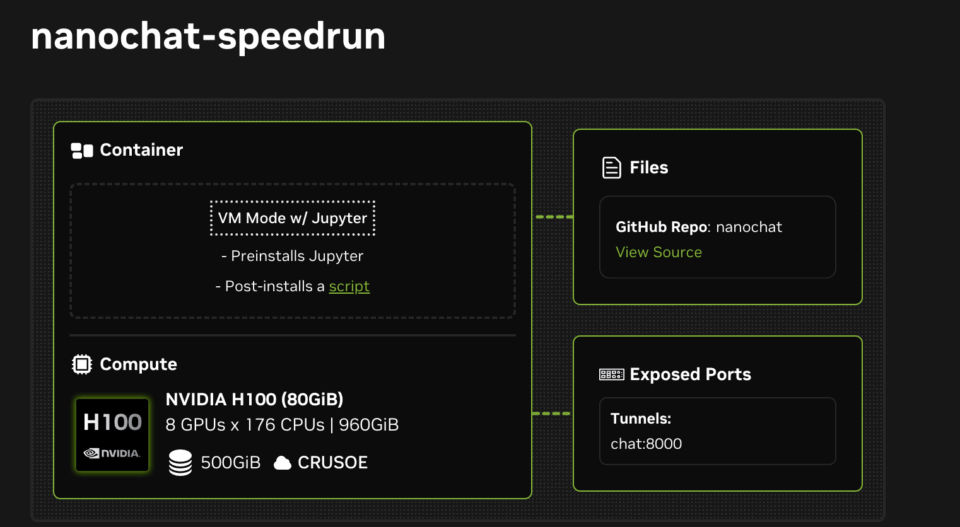
Computer scientist Andrej Karpathy recently introduced Nanochat, calling it “the best ChatGPT that $100 can buy.” Nanochat is an open-source, full-stack large language model (LLM) implementation built for transparency and experimentation. In about 8,000 lines of minimal, dependency-light code, Nanochat runs the entire LLM pipeline — from tokenization and pretraining to fine-tuning, inference and chat — all through a simple web user interface.
NVIDIA is supporting Karpathy’s open-source Nanochat project by releasing two NVIDIA Launchables, making it easy to deploy and experiment with Nanochat across various NVIDIA GPUs.
With NVIDIA Launchables, developers can train and interact with their own conversational model in hours with a single click. The Launchables dynamically support different-sized GPUs — including NVIDIA H100 and L40S GPUs — on various clouds without need for modification. They also automatically work on any eight-GPU instance on NVIDIA Brev, so developers can get compute access immediately.
The first 10 users to deploy these Launchables will also receive free compute access to NVIDIA H100 or L40S GPUs.
Start training with Nanochat by deploying a Launchable:
Andrej Karpathy’s Next Experiments Begin With NVIDIA DGX Spark
Today, Karpathy received an NVIDIA DGX Spark — the world’s smallest AI supercomputer, designed to bring the power of Blackwell right to a developer’s desktop. With up to a petaflop of AI processing power and 128GB of unified memory in a compact form factor, DGX Spark empowers innovators like Karpathy to experiment, fine-tune and run massive models locally.
Building the Future of AI With PyTorch and NVIDIA 🔗
PyTorch, the fastest-growing AI framework, derives its performance from the NVIDIA CUDA platform and uses the Python programming language to unlock developer productivity. This year, NVIDIA added Python as a first-class language to the CUDA platform, giving the PyTorch developer community greater access to CUDA.
CUDA Python includes key components that make GPU acceleration in Python easier than ever, with built-in support for kernel fusion, extension module integration and simplified packaging for fast deployment.
Following PyTorch’s open collaboration model, CUDA Python is available on GitHub and PyPI.

Every month, developers worldwide download hundreds of millions of NVIDIA libraries — including CUDA, cuDNN, cuBLAS and CUTLASS — mostly within Python and PyTorch environments. CUDA Python provides nvmath-python, a new library that acts as the bridge between Python code and these highly optimized GPU libraries.
Plus, kernel enhancements and support for next-generation frameworks make NVIDIA accelerated computing more efficient, adaptable and widely accessible.
NVIDIA maintains a long-standing collaboration with the PyTorch community through open-source contributions and technical leadership, as well as by sponsoring and participating in community events and activations.
At PyTorch Conference 2025 in San Francisco, NVIDIA will host a keynote address, five technical sessions and nine poster presentations.
NVIDIA’s on the ground at Open Source AI Week. Stay tuned for a celebration highlighting the spirit of innovation, collaboration and community that drives open-source AI forward. Follow NVIDIA AI Developer on social channels for additional news and insights.
NVIDIA Spotlights Open Source Innovation 🔗
Open Source AI Week kicks off on Monday with a series of hackathons, workshops and meetups spotlighting the latest advances in AI, machine learning and open-source innovation.
The event brings together leading organizations, researchers and open-source communities to share knowledge, collaborate on tools and explore how openness accelerates AI development.
NVIDIA continues to expand access to advanced AI innovation by providing open-source tools, models and datasets designed to empower developers. With more than 1,000 open-source tools on NVIDIA GitHub repositories and over 500 models and 100 datasets on the NVIDIA Hugging Face collections, NVIDIA is accelerating the pace of open, collaborative AI development.
Over the past year, NVIDIA has become the top contributor in Hugging Face repositories, reflecting a deep commitment to sharing models, frameworks and research that empower the community.
Openly available models, tools and datasets are essential to driving innovation and progress. By empowering anyone to use, modify and share technology, it fosters transparency and accelerates discovery, fueling breakthroughs that benefit both industry and communities alike. That’s why NVIDIA is committed to supporting the open source ecosystem.
We’re on the ground all week — stay tuned for a celebration highlighting the spirit of innovation, collaboration and community that drives open-source AI forward, with the PyTorch Conference serving as the flagship event.