Editor’s note: This post is part of Into the Omniverse, a series focused on how developers, 3D practitioners and enterprises can transform their workflows using the latest advancements in OpenUSD and NVIDIA Omniverse.
Physical AI is moving from research labs into the real world, powering intelligent robots and autonomous vehicles (AVs) — such as robotaxis — that must reliably sense, reason and act amid unpredictable conditions.
To safely scale these systems, developers need workflows that connect real-world data, high-fidelity simulation and robust AI models atop the common foundation provided by the OpenUSD framework.
The recently published OpenUSD Core Specification 1.0, OpenUSD — aka Universal Scene Description — now defines standard data types, file formats and composition behaviors, giving developers predictable, interoperable USD pipelines as they scale autonomous systems.
Powered by OpenUSD, NVIDIA Omniverse libraries combine NVIDIA RTX rendering, physics simulation and efficient runtimes to create digital twins and simulation-ready (SimReady) assets that accurately reflect real-world environments for synthetic data generation and testing.
NVIDIA Cosmos world foundation models can run on top of these simulations to amplify data variation, generating new weather, lighting and terrain conditions from the same scenes so teams can safely cover rare and challenging edge cases.
Learn more by watching the OpenUSD livestream today at 11 a.m. PT or in replay, part of the NVIDIA Omniverse OpenUSD Insiders series:
In addition, advancements in synthetic data generation, multimodal datasets and SimReady workflows are now converging with the NVIDIA Halos framework for AV safety, creating a standards-based path to safer, faster, more cost-effective deployment of next-generation autonomous machines.
Building the Foundation for Safe Physical AI
Open Standards and SimReady Assets
The OpenUSD Core Specification 1.0 establishes the standard data models and behaviors that underpin SimReady assets, enabling developers to build interoperable simulation pipelines for AI factories and robotics on OpenUSD.
Built on this foundation, SimReady 3D assets can be reused across tools and teams and loaded directly into NVIDIA Isaac Sim, where USDPhysics colliders, rigid body dynamics and composition-arc–based variants let teams test robots in virtual facilities that closely mirror real operations.
Open-Source Learning
The Learn OpenUSD curriculum is now open source and available on GitHub, enabling contributors to localize and adapt templates, exercises and content for different audiences, languages and use cases. This gives educators a ready-made foundation to onboard new teams into OpenUSD-centric simulation workflows.
Generative Worlds as Safety Multiplier
Gaussian splatting — a technique that uses editable 3D elements to render environments quickly and with high fidelity — and world models are accelerating simulation pipelines for safe robotics testing and validation.
At SIGGRAPH Asia, the NVIDIA Research team introduced Play4D, a streaming pipeline that enables 4D Gaussian splatting to accurately render dynamic scenes and improve realism.
Spatial intelligence company World Labs is using its Marble generative world model with NVIDIA Isaac Sim and Omniverse NuRec so researchers can turn text prompts and sample images into photorealistic, Gaussian-based physics-ready 3D environments in hours instead of weeks.
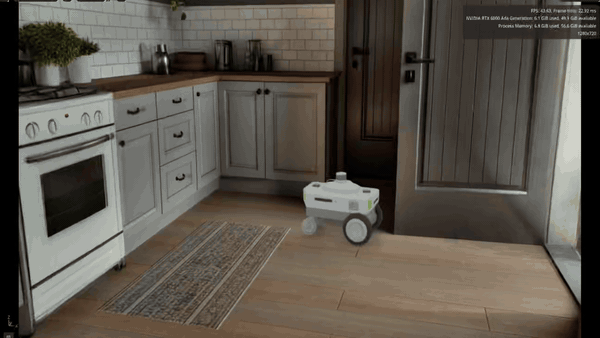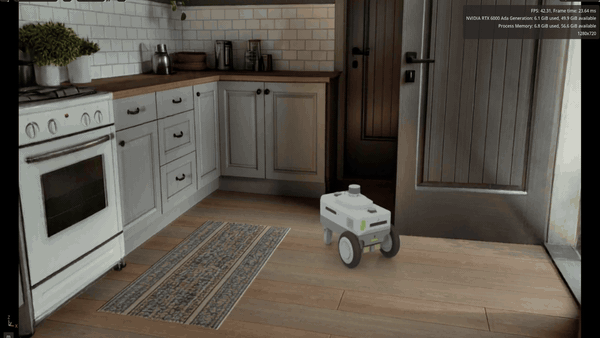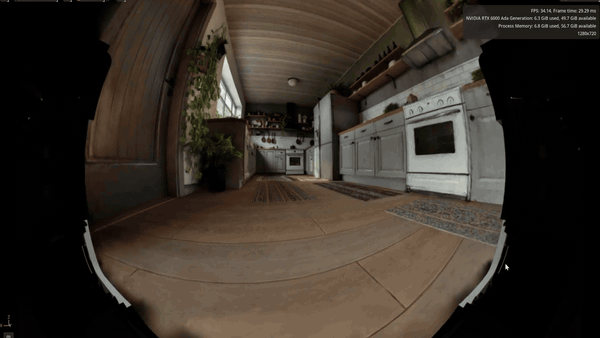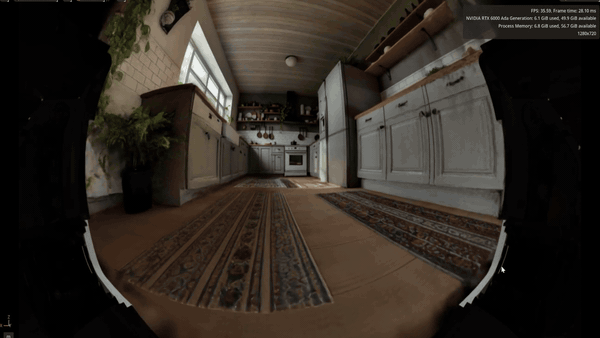
Those worlds can then be used for physical AI training, testing and sim-to-real transfer. This high-fidelity simulation workflow expands the range of scenarios robots can practice in while keeping experimentation safely in simulation.
Lightwheel Helps Teams Scale Robot Training With SimReady Assets
Powered by OpenUSD, Lightwheel’s SimReady asset library includes a common scene description layer, making it easy to assemble high-fidelity digital twins for robots. The SimReady assets are embedded with precise geometry, materials and validated physical properties, which can be loaded directly into NVIDIA Isaac Sim and Isaac Lab for robot training. This allows robots to experience realistic contacts, dynamics and sensor feedback as they learn.
End-to-End Autonomous Vehicle Safety
End-to-end autonomous vehicle safety advancements are accelerating with new research, open frameworks and inspection services that make validation more rigorous and scalable.
NVIDIA researchers, with collaborators at Harvard University and Stanford University, recently introduced the Sim2Val framework to statistically combine real-world and simulated test results, reducing AV developers’ need for costly physical mileage while demonstrating how robotaxis and AVs can behave safely across rare and safety-critical scenarios.
Learn more by watching NVIDIA’s “Safety in the Loop” livestream:
These innovations are complemented by a new, open-source NVIDIA Omniverse NuRec Fixer, a Cosmos-based model trained on AV data that removes artifacts in neural reconstructions to produce higher-quality SimReady assets.
To align these advances with rigorous global standards, the NVIDIA Halos AI Systems Inspection Lab — accredited by ANAB — provides impartial inspection and certification of Halos elements across robotaxi fleets, AV stacks, sensors and manufacturer platforms through the Halos Certification Program.
AV Ecosystem Leaders Putting Physical AI Safety to Work
Bosch, Nuro and Wayve are among the first participants in the NVIDIA Halos AI Systems Inspection Lab, which aims to accelerate the safe, large-scale deployment of robotaxi fleets. Onsemi, which makes sensor systems for AVs, industrial automation and medical applications, has recently become the first company to pass inspection for the NVIDIA Halos AI Systems Inspection Lab.
The open-source CARLA simulator integrates NVIDIA NuRec and Cosmos Transfer to generate reconstructed drives and diverse scenario variations, while Voxel51’s FiftyOne engine, linked to Cosmos Dataset Search, NuRec and Cosmos Transfer, helps teams curate, annotate and evaluate multimodal datasets across the AV pipeline.
Mcity at the University of Michigan is enhancing the digital twin of its 32-acre AV test facility using Omniverse libraries and technologies. The team is integrating the NVIDIA Blueprint for AV simulation and Omniverse Sensor RTX application programming interfaces to create physics-based models of camera, lidar, radar and ultrasonic sensors.
By aligning real sensor recordings with high-fidelity simulated data and sharing assets openly, Mcity enables safe, repeatable testing of rare and hazardous driving scenarios before vehicles operate on public roads.
Get Plugged Into the World of OpenUSD and Physical AI Safety
Learn more about OpenUSD, NVIDIA Halos and physical AI safety by exploring these resources:
- Watch the on-demand NVIDIA GTC session, “Reconstructing Reality: Simulating Indoor and Outdoor Environments for Physical AI.”
- Visit the NVIDIA Halos AI Systems Inspection Lab webpage.
- Follow the NVIDIA DRIVE LinkedIn newsletter: “NVIDIA Safety in the Loop.”
- Read the corporate blog explainer: How AI Is Unlocking Level 4 Autonomy.
- Get started with the Learn OpenUSD curriculum, now open source.
Stay up to date by subscribing to NVIDIA news, joining the community and following NVIDIA Omniverse on Instagram, LinkedIn, Medium and X.
