Picture this: dozens of talks about AI in medical imaging, presented by experts from top radiology departments and academic medical centers around the world, all available free online.
That’s just a slice of GTC Digital, a vast library of live and on-demand webinars, training sessions and office hours from NVIDIA’s GPU Technology Conference.
Healthcare innovators across radiology, genomics, microscopy and more will share the latest AI and GPU-accelerated advancements in their fields through talks on GTC Digital.
Researchers in Sydney, Australia, are using AI to analyze brain scans. In Massachusetts, another is segmenting the prostate gland from ultrasound images to help doctors fine-tune radiation doses. And in Munich, Germany, they’re streamlining radiology reports to foster real-time reporting.
Read more about these standout speakers advancing the use of deep learning in medical imaging worldwide below. And register for GTC Digital for free to see the whole healthcare lineup.
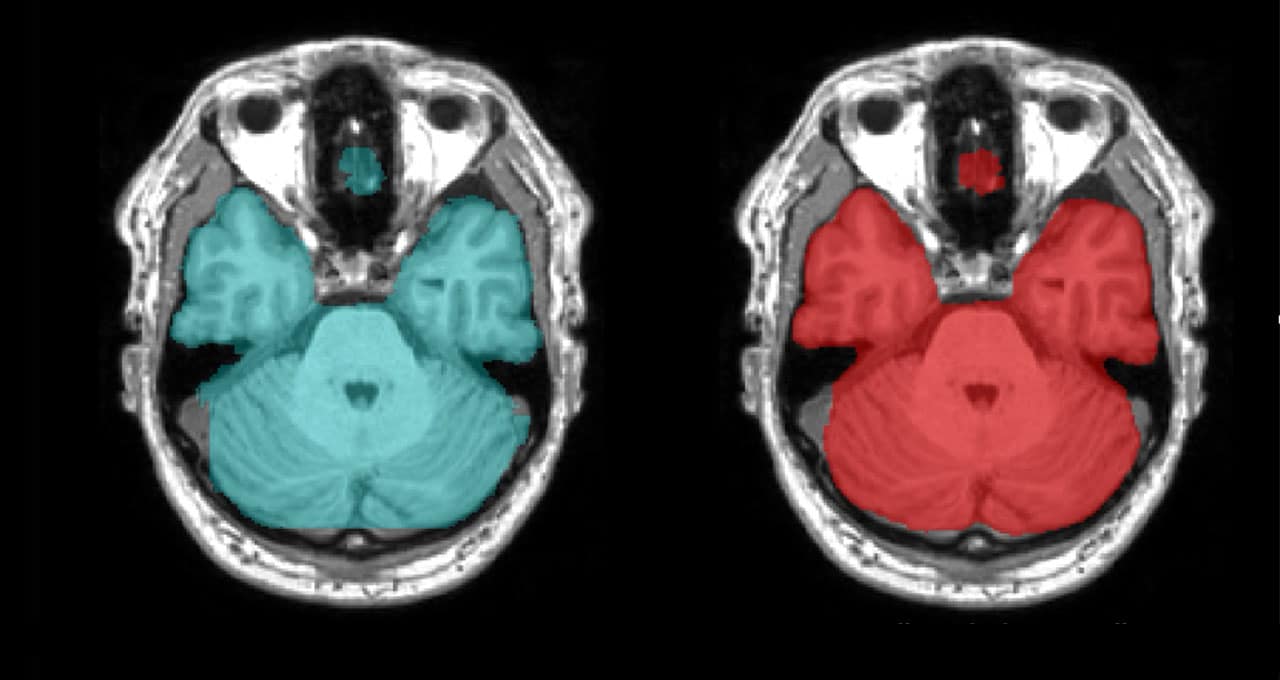
Mental Math: Australian Center Uses AI to Analyze Brain Scans
When studying neurodegenerative disease, quantifying brain tissue loss over time helps physicians and clinical trialists monitor disease progression. Radiologists typically inspect brain scans visually and classify the brain shrinkage as “moderate” or “severe” — a qualitative assessment. With accelerated computing, brain tissue loss can instead be measured precisely and quantitatively, without losing time.
The Sydney Neuroimaging Analysis Centre conducts neuroimaging research as well as commercial image analysis for clinical research trials. SNAC will share at GTC Digital how it uses AI and NVIDIA GPUs to accelerate AI tools that automate laborious analysis tasks in their research workflow.
One model precisely isolates brain images from head scans, segmenting brain lesions for multiple sclerosis cases. The AI reduces the time to segment and determine the volume of brain lesions from up to 15 minutes for a manual examination down to just three seconds, regardless of the number or volume of lesions.
“NVIDIA GPUs and DGX systems are the core of our AI platform, and are transforming the delivery of clinical and research radiology with our AI innovation,” said Tim Wang, director of operations at SNAC. “We are particularly excited by the application of this technology to brain imaging.”
SNAC uses the NVIDIA Clara Train SDK’s AI-assisted annotation tools for model development and the NVIDIA Clara Deploy SDK for integration with clinical and research workflows. It’s also exploring the NVIDIA Clara platform as a tool for federated learning. The center relies on the NVIDIA DGX-1 server, NVIDIA DGX Station and GPU-powered PC workstations for both training and inference of its AI algorithms.
Harvard Researcher Applies AI to Prostate Cancer Therapy
Around one in nine men is diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point during his life. Medical imaging tools like ultrasound and MRI are key methods doctors use to check prostate health and plan for surgery and radiotherapy.
Davood Karimi, a research fellow at Harvard Medical School, is developing deep learning models to more quickly and accurately segment the prostate gland from ultrasound images — a difficult task because the boundaries of the prostate are often either not visible or blurry in ultrasound images.
“Accurate segmentation is necessary to make sure radiologists can deliver the needed radiation dose to the prostate, but avoid damaging critical nearby structures like the rectum or bladder,” he said.
In his GTC Digital talk, Karimi will do a deep dive into a research paper he presented at the prestigious MICCAI healthcare conference last year. Using an NVIDIA TITAN GPU, Karimi has accelerated neural network inference to under a second per scan, while improving accuracy over current segmentation techniques radiologists use.
German Company Streamlines Radiology Reports with NVIDIA Clara
Healthcare providers worldwide record their analyses of patient data, including medical images, into text-based reports. But no two radiologists or hospitals do it exactly the same.
Munich-based Smart Reporting GmbH aims to streamline and standardize the reporting workflow for radiologists. The company uses a structured reporting interface that organizes patient data and doctor’s notes into a consistent format.
Smart Reporting uses the NVIDIA Clara platform to segment prostate cancer lesions from medical images. This image annotation is loaded into a draft diagnosis report that radiologists can approve, edit or reject before generating a final report to provide to surgeons and other healthcare professionals.
A member of the NVIDIA Inception virtual accelerator program, Smart Reporting is working with major healthcare organizations including Siemens Healthineers.
“When we release a prototype for radiologists in the clinic, it’ll be essential to have almost real-time reporting,” said Dominik Noerenberg, the company’s chief medical officer. “We’re able to see that speedup running on multi-GPU containers in NGC.”
Noerenberg and Alvaro Sanchez, principal software engineer at Smart Reporting, will present a talk on the advantages of AI-enhanced radiology workflows at GTC Digital.
See the full lineup of healthcare talks on GTC Digital and register for free.
Main image shows a side-by-side comparison of brain segmentation. Left image shows manual segmentation, while right shows AI segmentation. Image courtesy of Sydney Neuroimaging Analysis Centre.