Foxconn Taps NVIDIA to Accelerate Physical and Digital Robotics for Global Healthcare Industry
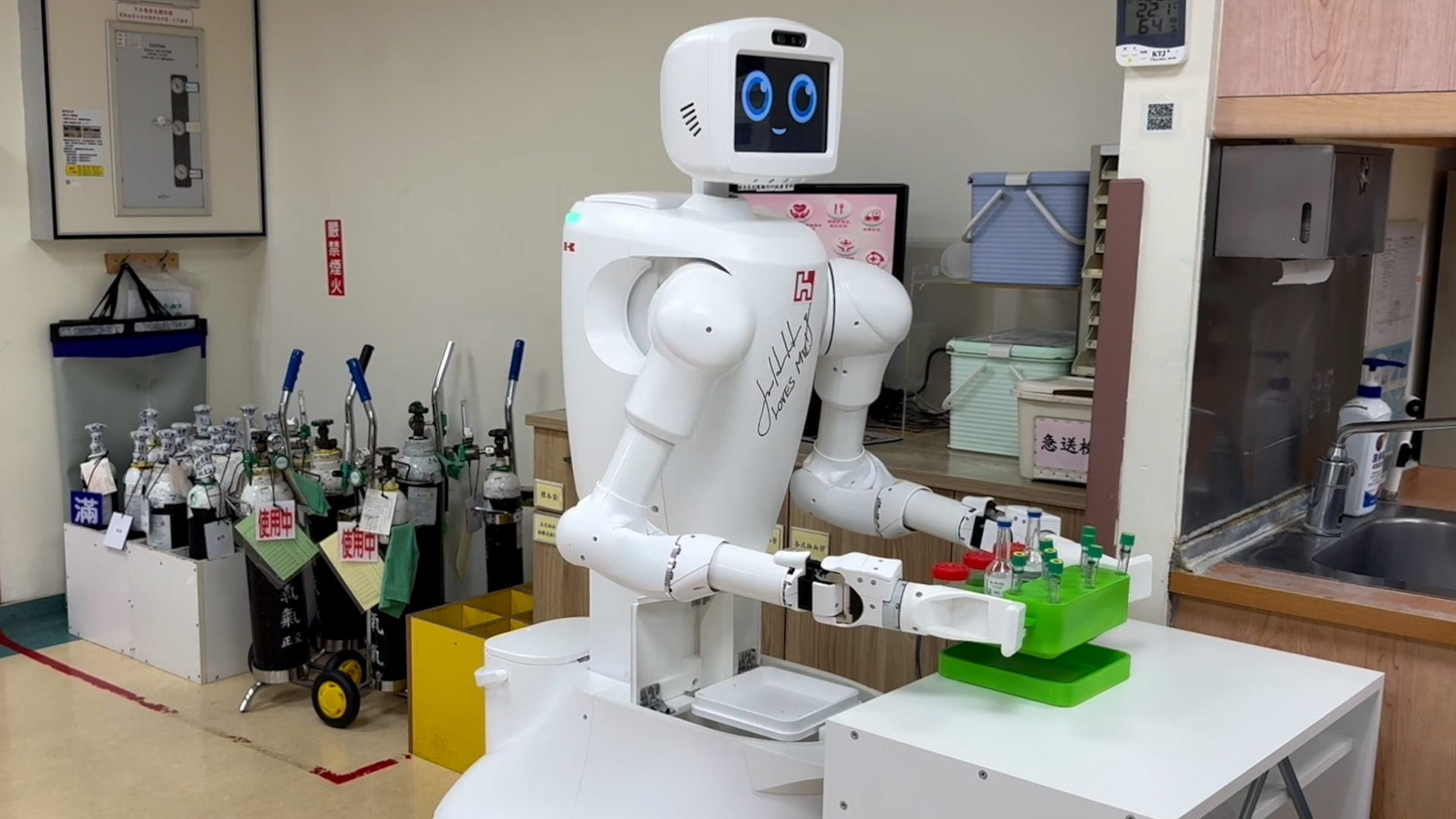

The global healthcare system is expected to face a shortage of 4.5 million nurses by 2030 — and one of the main causes is high burnout. Manufacturing giant Foxconn is helping ease the burden with NVIDIA-accelerated solutions like Nurabot, a collaborative nursing robot that offloads time-consuming, fatiguing tasks such as transporting medication and samples across the hospital.
Nurabot is just one of Foxconn’s smart hospital applications developed using NVIDIA technologies and deployed by Taiwan’s leading medical centers. Its other tools include AI models to support patient health monitoring and digital twins of hospital facilities to help management teams with design and planning.
Together, these applications can transform medical centers into smart hospitals powered by NVIDIA physical AI and its three-computer solution. First, massive AI models are trained and fine-tuned on supercomputers. Next, in simulation, digital twins are used for planning, testing and robotics training — and third, edge computing systems enable rapid AI inference on robots and sensors.
Taichung Veterans General Hospital (TCVGH), Baishatun Tung Hospital – Mazu Hospital, and Cardinal Tien Hospital are among the Taiwan-based healthcare institutions adopting Foxconn’s smart hospital solutions to support clinicians and advance patient care.
“Taiwan has a highly developed healthcare infrastructure with a strong push toward digital health transformation, creating the ideal environment for robotic integration,” said Shu-Fang Liu, deputy director of the nursing department at TCVGH, which is currently conducting a field trial with Nurabot. “Robots are augmenting our capabilities so we can provide more focused, meaningful care.”
Recognized as one of the world’s top 100 smart hospitals, TCVGH is developing multiple solutions to address the severe shortage of nursing personnel in Taiwan. In addition to implementing welfare policies to retain talent, the hospital is harnessing AI technology to ease the burden on frontline staff, noted Dr. Yun-Ching Fu, the hospital’s superintendent.
The hospital began working with Foxconn last year to codevelop the Nurabot collaborative nursing robots as part of its smart healthcare initiative led by Dr. Shih-An Chen, honorary superintendent at TCVGH.
Supporting Smart Hospitals From the Data Center to the Edge
Foxconn’s smart hospital solution begins in the data center, where high-performance compute is applied to develop large AI foundation models — like FoxBrain, a large language model (LLM) developed using the NVIDIA NeMo framework. Trained on NVIDIA Hopper GPUs, FoxBrain is capable of text-to-speech, automatic speech recognition and natural language processing.
The company is also using its Honhai Super AI Computing Center 1, which features NVIDIA DGX systems, to develop healthcare-specific AI models. Offered through Foxconn’s CoDoctor AI platform, powered by NVIDIA AI, these models improve diagnostic accuracy and optimize clinical workflows for tasks including retinal imaging, vital sign monitoring, arrhythmia screening and cancer screening.
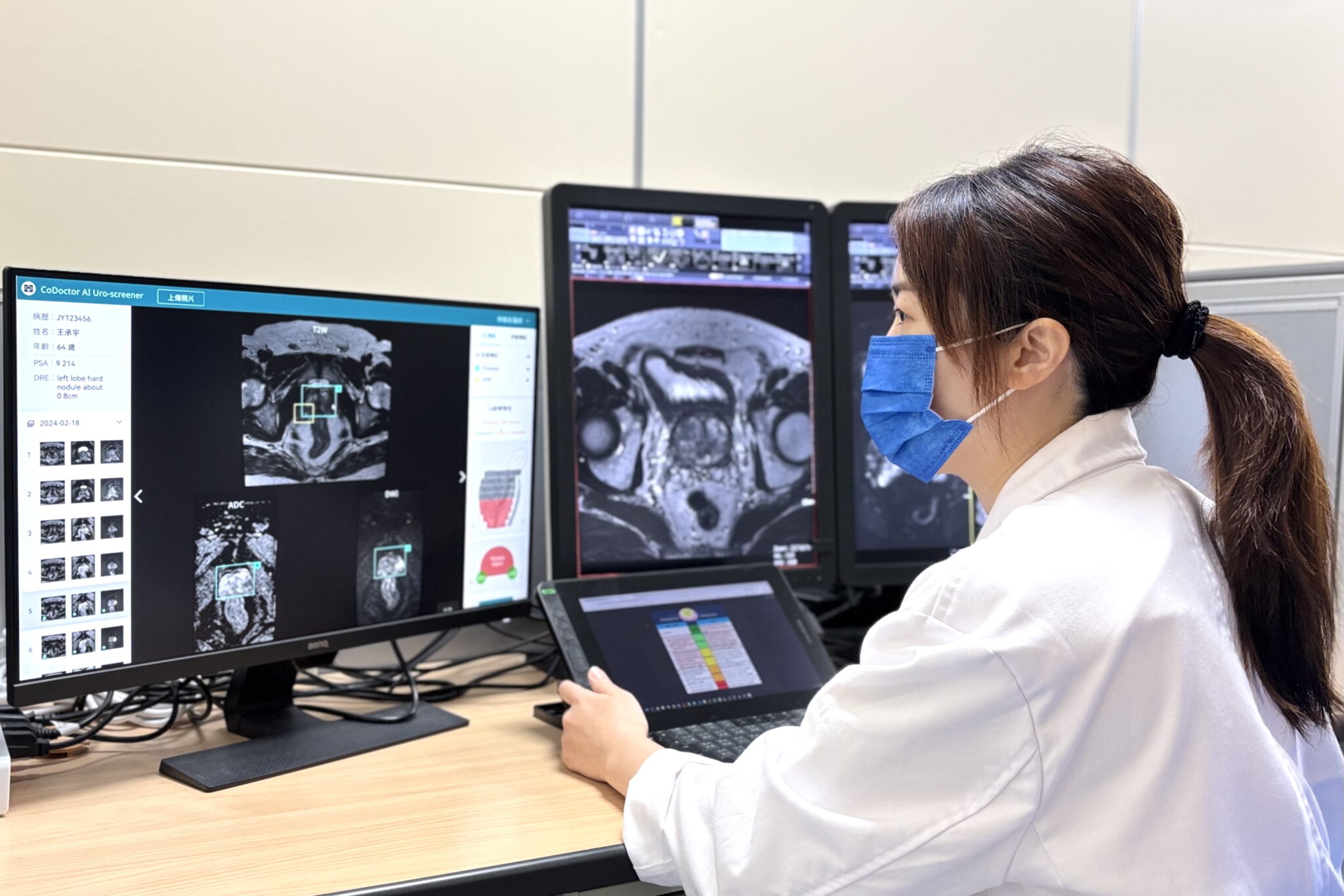
Foxconn is also working with medical centers to integrate the NVIDIA AI Blueprint for video search and summarization, which can analyze real-time video data to alert healthcare workers of medical events and generate visual summaries for hospital management teams.
It will contribute CoroSegmentater, its AI model for coronary artery segmentation, to the MONAI open-source medical imaging platform pioneered by NVIDIA and leading academic medical centers. The model, powered by MONAI’s Auto3DSeg framework for 3D medical image segmentation, can be used to support diagnostics, preoperative planning and patient education.
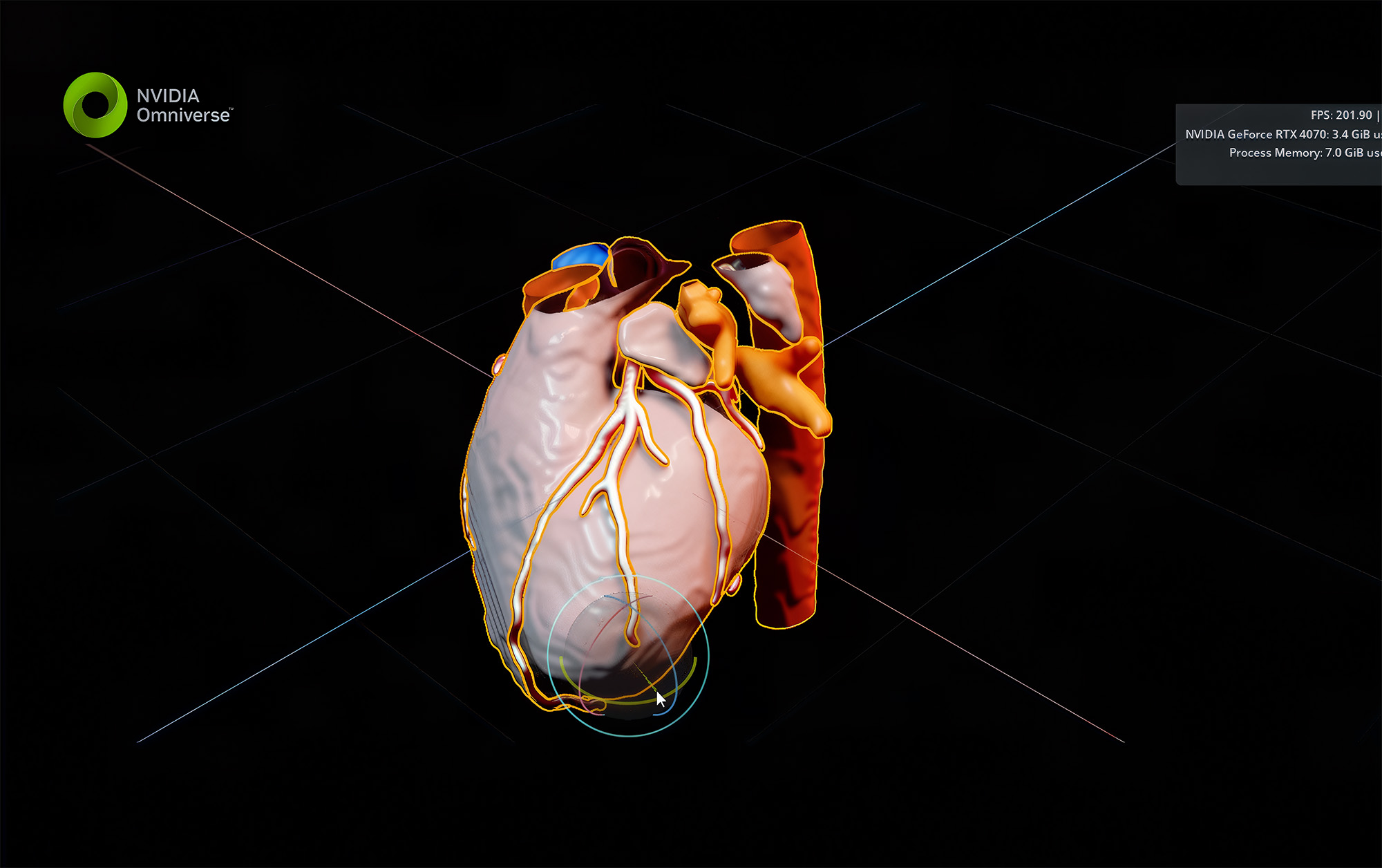
Clinical teams can visualize these segmentations on 3D visualizations of the heart and vascular system running on NVIDIA OVX servers with NVIDIA Isaac for Healthcare, built on the NVIDIA Omniverse platform. Foxconn has also used Omniverse to develop a tool that can simulate the effects of drug treatments on the tumors of breast cancer patients.
Beyond simulating biology, Foxconn is working with TCVGH, Baishatun Tung Hospital – Mazu Hospital, and Cardinal Tien Hospital to simulate healthcare facilities using NVIDIA Omniverse. With these physically accurate simulations, the hospitals are planning out the design of new facilities, making data-driven decisions to optimize operations and building simulations to train robots.
TCVGH, for instance, built a digital twin of one of its nursing stations and wards as a training ground for Nurabot — enabling the robotic system to practice navigating through virtual hallways before testing in the real world.
Taichung Veterans General Hospital Pilots Collaborative Nursing Robot
Nurabot — built by Foxconn and Japanese multinational company Kawasaki Heavy Industries — uses the FoxBrain LLM, virtual training with Isaac for Healthcare and onboard compute powered by the NVIDIA Holoscan sensor processing platform running on an NVIDIA Jetson Orin device.
Foxconn estimates that when deployed in clinical applications for delivering medication, transporting specimens and patrolling wards, Nurabot can reduce the workload of nurses by up to 30%.
“In one of our wards, we are using Nurabot to deliver wound care kits and health education materials to patient bedsides,” said Liu. “For nurses, having a robot assistant reduces physical fatigue, saving them multiple trips to supply rooms and allowing them to focus more on patients.”
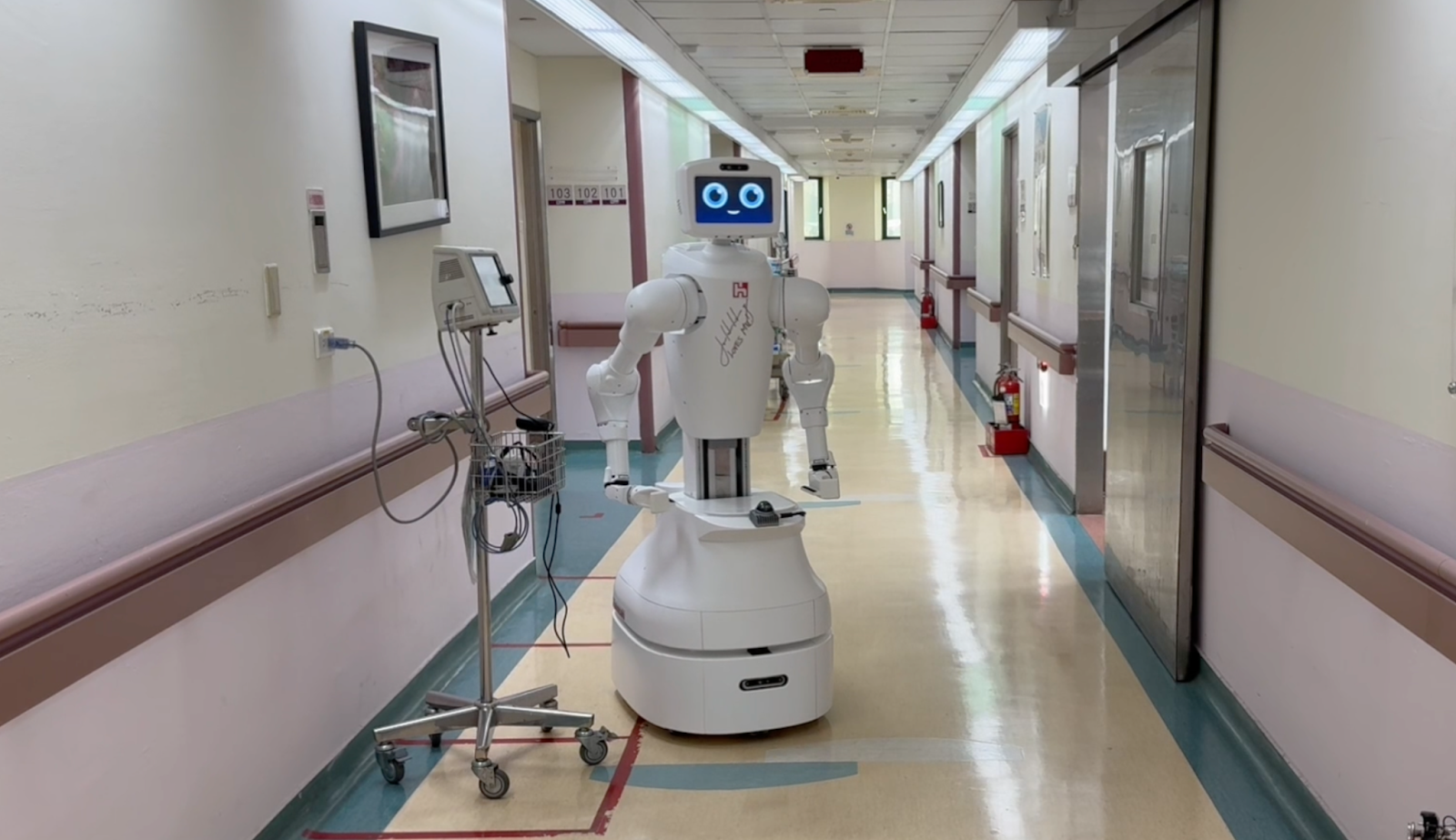

During visiting hours, Nurabot helps guide patients and visitors through the ward, reducing the administrative workload for frontline staff. And during night shifts, where hospitals operate with fewer staff, it can help pick up the slack.
Liu hopes the nursing robots will also be able to soon converse with patients in multiple languages, recognize individuals to enable personalized interactions, and help nurses move patients.
Someone with a lung condition, for example, may need the help of two nurses to get up from their hospital bed and move to a chair to perform breathing exercises. With the help of an assistant like Nurabot, the task might be accomplished with a single nurse, allowing the other to focus on caring for the rest of the ward.
TCVGH’s field trial with Nurabot is drawing positive reactions from nurses and patients — and the hospital expects to deploy dozens of robot units to support its nursing team by the end of this year.
NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang highlighted Foxconn’s solutions for healthcare during his keynote address today at the COMPUTEX trade show in Taipei. These initiatives will also be detailed at GTC Taipei, taking place May 21-22.