GTC brought together dozens of healthcare innovators to present their work — and announce new AI-accelerated applications and medical devices.
More than 200,000 people registered for last week’s online conference, where they attended hundreds of sessions spanning industries. The healthcare track included speakers from AstraZeneca, Mayo Clinic, Medtronic, Netherlands Cancer Institute and Pfizer, as well as more than 50 NVIDIA Inception startups.
Here’s some of the healthcare news shared at the show by NVIDIA, leading research institutions, and AI and medical device companies:
Breakthroughs in Transformer Models to Parse Medical Text
Janssen, the pharmaceutical arm of Johnson & Johnson, shared its intelligent automation work using natural language processing models to scan medical literature that reports patients who may have experienced possible side effects. The latest version of the Janssen AI platform, which uses a customized version of BioMegatron using the NVIDIA NeMo framework, was set up in late 2021 to help accelerate the shortlisting of medical literature for human review to analyze drug safety.
Adopting BioMegatron improved overall model accuracy by 12 percent. The Janssen team also uses NVIDIA TensorRT and NVIDIA Triton to optimize AI models for inference, which doubled compute throughput and efficiency.
Drug discovery company Absci presented two research breakthroughs for antibody design in a GTC session presented by its lead AI scientist, Joshua Meier. Absci is accelerating its neural networks using optimized graph and transformer kernels running on NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs. Absci is a member of NVIDIA Inception, a program designed to nurture cutting-edge startups.
One of the company’s machine learning models was able to predict how strongly different variants of trastuzumab — an antibody used to treat breast, stomach and esophageal cancer — could bind with a target. Another model was found to measure developability, which represents how likely a drug candidate is to succeed in testing and clinical development.
The University of Florida’s academic health center, UF Health, collaborated with NVIDIA on SynGatorTron, a neural network that generates synthetic clinical data. This synthetic data can be used to train other AI models for healthcare, alleviating privacy concerns around patient data while offering a way to augment health records so that historically underserved populations are better represented.
Both the original GatorTron model, announced last year, and GatorTron-S — a Megatron BERT model trained on synthetic discharge summaries generated by SynGatorTron — are available to developers on the NGC software and container hub.
And in the GTC talk “Accelerating Healthcare Innovation with AI,” NVIDIA announced that the next iteration of the MegaMolBART transformer model for cheminformatics, built with the NVIDIA Megatron-LM framework, will be available next month. The model achieves nearly 99 percent novelty for generated molecules.
Medical Device Companies, Healthcare Researchers Adopt NVIDIA Solutions
Genomic sequencing company Oxford Nanopore Technologies, an Inception alum, announced that its PromethION compute towers for ultra-high-throughput sequencing will now be powered by NVIDIA DGX Station A100 systems, boosting basecalling speed by more than 50 percent compared to previous hardware. The increased processing power will enable PromethION users working on large sequencing projects to simplify their workflows while achieving more than 99 percent raw read accuracy using neural networks.
To support whole genome analysis, researchers can get started with the ultrarapid nanopore analysis pipeline now on NGC.
And NVIDIA unveiled Clara Holoscan MGX, a medical-grade platform for real-time AI applications at the edge, specifically designed to meet the industry’s regulatory standards. Built for medical device developers, the platform includes the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin module, RTX A6000 GPU and ConnectX-7 SmartNIC network adapter.
Embedded computing system manufacturer Dedicated Computing announced an AI platform called M1000 that is initially designed for real-time AI inference in endoscopy applications and based on NVIDIA Clara Holoscan MGX. And Onyx Healthcare revealed ACCEL-JS2000, a system based on the Clara Holoscan MGX reference design that can be used in applications including surgery, radiation therapy and medical imaging.
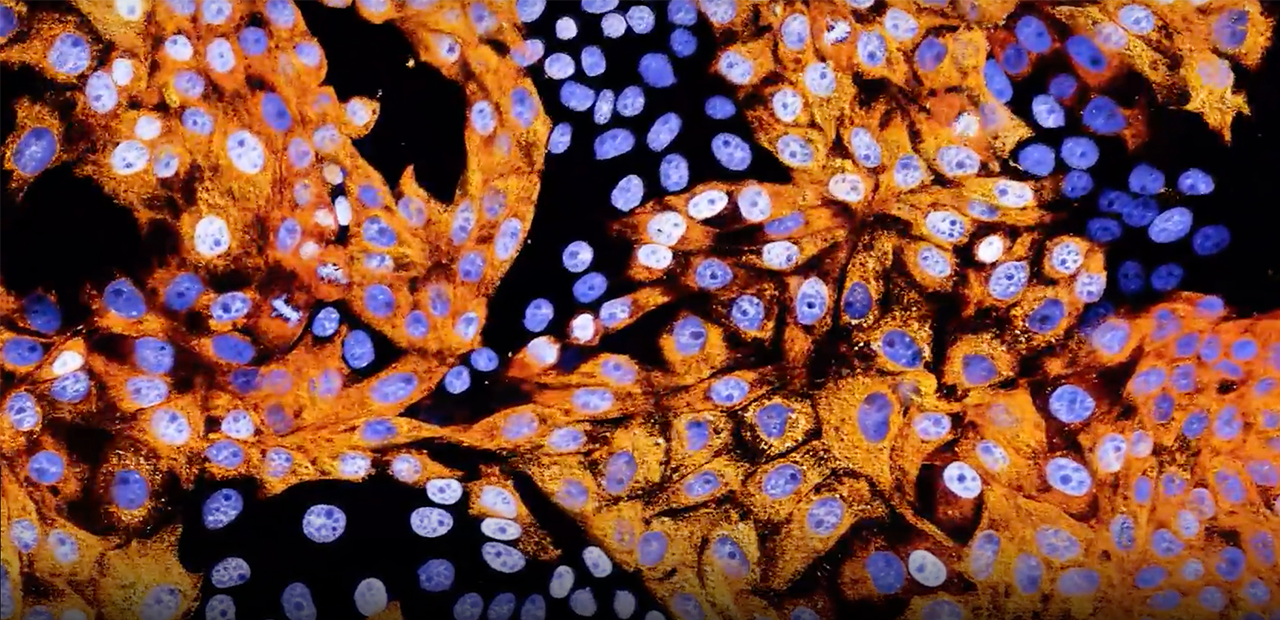
Researchers at the Advanced Bioimaging Center at UC Berkeley are already using NVIDIA Clara Holoscan for lattice lightsheet microscopy, a technique that allows scientists to capture videos of living cells over long periods of time. Using AI and the NVIDIA IndeX software development kit for volumetric visualization, the researchers can process and visualize streaming data in real time, instead of taking days.
Watch the GTC talk “Accelerating Healthcare Innovation with AI” for more on these announcements. Check out the GTC keynote address by NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang below:
Subscribe to NVIDIA healthcare news.
Main image courtesy of the Advanced Bioimaging Center at UC Berkeley.